Feasibility study of portable multi-energy computed tomography with photon-counting detector for preclinical and clinical applications
- PMID: 34815501
- PMCID: PMC8611013
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-02210-5
Feasibility study of portable multi-energy computed tomography with photon-counting detector for preclinical and clinical applications
Abstract
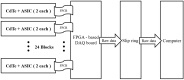
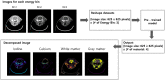
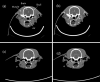
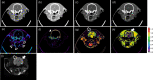
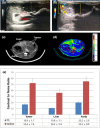
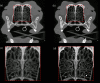
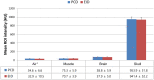
In this study, preclinical experiments were performed with an in-house developed prototypal photon-counting detector computed tomography (PCD CT) system. The performance of the system was compared with the conventional energy-integrating detector (EID)-based CT, concerning the basic image quality biomarkers and the respective capacities for material separation. The pre- and the post-contrast axial images of a canine brain captured by the PCD CT and EID CT systems were found to be visually similar. Multi-energy images were acquired using the PCD CT system, and machine learning-based material decomposition was performed to segment the white and gray matters for the first time in soft tissue segmentation. Furthermore, to accommodate clinical applications that require high resolution acquisitions, a small, native, high-resolution (HR) detector was implemented on the PCD CT system, and its performance was evaluated based on animal experiments. The HR acquisition mode improved the spatial resolution and delineation of the fine structures in the canine's nasal turbinates compared to the standard mode. Clinical applications that rely on high-spatial resolution expectedly will also benefit from this resolution-enhancing function. The results demonstrate the potential impact on the brain tissue segmentation, improved detection of the liver tumors, and capacity to reconstruct high-resolution images both preclinically and clinically.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests. CL.L., K.H., N.K., K.H., S.L., J.P., KY.L., Y.C., M.C. are employees of Samsung Electronics.
Figures