Recent progress and new challenges in modeling of human pluripotent stem cell-derived blood-brain barrier
- PMID: 34815809
- PMCID: PMC8581424
- DOI: 10.7150/thno.63195
Recent progress and new challenges in modeling of human pluripotent stem cell-derived blood-brain barrier
Abstract
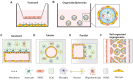
The blood-brain barrier (BBB) is a semipermeable unit that serves to vascularize the central nervous system (CNS) while tightly regulating the movement of molecules, ions, and cells between the blood and the brain. The BBB precisely controls brain homeostasis and protects the neural tissue from toxins and pathogens. The BBB is coordinated by a tight monolayer of brain microvascular endothelial cells, which is subsequently supported by mural cells, astrocytes, and surrounding neuronal cells that regulate the barrier function with a series of specialized properties. Dysfunction of barrier properties is an important pathological feature in the progression of various neurological diseases. In vitro BBB models recapitulating the physiological and diseased states are important tools to understand the pathological mechanism and to serve as a platform to screen potential drugs. Recent advances in this field have stemmed from the use of pluripotent stem cells (PSCs). Various cell types of the BBB such as brain microvascular endothelial cells (BMECs), pericytes, and astrocytes have been derived from PSCs and synergistically incorporated to model the complex BBB structure in vitro. In this review, we summarize the most recent protocols and techniques for the differentiation of major cell types of the BBB. We also discuss the progress of BBB modeling by using PSC-derived cells and perspectives on how to reproduce more natural BBBs in vitro.
Keywords: blood-brain barrier; brain microvascular endothelial cells; disease modeling.; neurovascular unit; pluripotent stem cells.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures

References
-
- Ghose AK, Viswanadhan VN, Wendoloski JJ. A knowledge-based approach in designing combinatorial or medicinal chemistry libraries for drug discovery. 1. A qualitative and quantitative characterization of known drug databases. J Comb Chem. 1999;1:55–68. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

