Sentiment Analysis in Social Media Data for Depression Detection Using Artificial Intelligence: A Review
- PMID: 34816124
- PMCID: PMC8603338
- DOI: 10.1007/s42979-021-00958-1
Sentiment Analysis in Social Media Data for Depression Detection Using Artificial Intelligence: A Review
Abstract
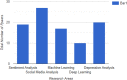
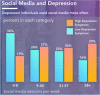
Sentiment analysis is an emerging trend nowadays to understand people's sentiments in multiple situations in their quotidian life. Social media data would be utilized for the entire process ie the analysis and classification processes and it consists of text data and emoticons, emojis, etc. Many experiments were conducted in the antecedent studies utilizing Binary and Ternary Classification whereas Multi-class Classification gives more precise and precise Classification. In Multi-class Classification, the data would be divided into multiple sub-classes predicated on the polarities. Machine Learning and Deep Learning Techniques would be utilized for the classification process. Utilizing Social media, sentiment levels can be monitored or analysed. This paper shows a review of the sentiment analysis on Social media data for apprehensiveness or dejection detection utilizing various artificial intelligence techniques. In the survey, it was optically canvassed that social media data which consists of texts,emoticons and emojis were utilized for the sentiment identification utilizing various artificial intelligence techniques. Multi Class Classification with Deep Learning Algorithm shows higher precision value during the sentiment analysis.
Keywords: Deep learning; Depression; Emoticons & Emojis; Feature extraction; Machine learning; Multiclass classification; Natural language processing; Sentiment analysis; Social network analysis.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestAll Authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Chen B, Cheng L, Chen R, Huang Q, Phoebe Chen Y-P. Deep neural networks for multiclass sentiment classification. In: IEEE 20th International Conference on high performance computing and communications, IEEE 16th International Conference on Smart City, IEEE 4th International Conference on Data Science and Systems 2018; pp. 854–59.
-
- Sethi M, Pande S, Trar P, Soni P. Sentiment identification in COVID-19 specific tweets. In: International Conference on electronics and sustainable communication systems (ICESC 2020), pp. 509–16, 10.1109/ICESC48915.2020.9155674.
-
- Kundale JU, Kulkarni NJ. Language independent multi-class sentiment analysis. In: 5th International Conference on computing communication control and automation (ICCUBEA), 2019; pp. 1–7, 10.1109/ICCUBEA47591.2019.9128383.
-
- Ruz GA, Henriquez PA, Mascareno A. Sentiment analysis of Twitter data during critical events through Bayesian networks classifiers. Future Gener Comput Syst. 2020;106:92–104. doi: 10.1016/j.future.2020.01.005. - DOI
-
- Yang X, McEwen R, Ong LR, Zihayat M. A big data analytics framework for detecting user-level depression from social networks. Int J Inf Manag. 2020;54:102141. doi: 10.1016/j.ijinfomgt.2020.102141. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources