Fine Particulate Matter Induces Childhood Asthma Attacks via Extracellular Vesicle-Packaged Let-7i-5p-Mediated Modulation of the MAPK Signaling Pathway
- PMID: 34816611
- PMCID: PMC8787417
- DOI: 10.1002/advs.202102460
Fine Particulate Matter Induces Childhood Asthma Attacks via Extracellular Vesicle-Packaged Let-7i-5p-Mediated Modulation of the MAPK Signaling Pathway
Abstract
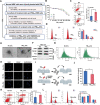
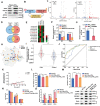
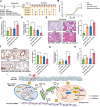
Fine particulate matter less than 2.5 µm in diameter (PM2.5 ) is a major risk factor for acute asthma attacks in children. However, the biological mechanism underlying this association remains unclear. In the present study, PM2.5 -treated HBE cells-secreted extracellular vesicles (PM2.5 -EVs) caused cytotoxicity in "horizontal" HBE cells and increased the contractility of "longitudinal" sensitive human bronchial smooth muscle cells (HBSMCs). RNA sequencing showed that let-7i-5p is significantly overexpressed in PM2.5 -EVs and asthmatic plasma; additionally, its level is correlated with PM2.5 exposure in children with asthma. The combination of EV-packaged let-7i-5p and the traditional clinical biomarker IgE exhibits the best diagnostic performance (area under the curve [AUC] = 0.855, 95% CI = 0.786-0.923). Mechanistically, let-7i-5p is packaged into PM2.5 -EVs by interacting with ELAVL1 and internalized by both "horizontal" recipient HBE cells and "longitudinal" recipient-sensitive HBSMCs, with subsequent activation of the MAPK signaling pathway via suppression of its target DUSP1. Furthermore, an injection of EV-packaged let-7i-5p into PM2.5 -treated juvenile mice aggravated asthma symptoms. This comprehensive study deciphered the remodeling of the extracellular environment mediated by the secretion of let-7i-5p-enriched EVs during PM2.5 -induced asthma attacks and identified plasma EV-packaged let-7i-5p as a novel predictor of childhood asthma.
Keywords: MAPK signaling pathway; PM2.5; childhood asthma; extracellular vesicles; let-7i-5p.
© 2021 The Authors. Advanced Science published by Wiley-VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Extracellular vesicles-encapsulated let-7i shed from bone mesenchymal stem cells suppress lung cancer via KDM3A/DCLK1/FXYD3 axis.J Cell Mol Med. 2021 Feb;25(4):1911-1926. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.15866. Epub 2020 Dec 22. J Cell Mol Med. 2021. PMID: 33350586 Free PMC article.
-
Mesenchymal Stem Cells Attenuate Renal Fibrosis via Exosomes-Mediated Delivery of microRNA Let-7i-5p Antagomir.Int J Nanomedicine. 2021 May 25;16:3565-3578. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S299969. eCollection 2021. Int J Nanomedicine. 2021. PMID: 34079249 Free PMC article.
-
MiR-451a and let-7i-5p loaded extracellular vesicles attenuate heme-induced inflammation in hiPSC-derived endothelial cells.Front Immunol. 2022 Dec 22;13:1082414. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1082414. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36618355 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular Vesicles and Asthma-More Than Just a Co-Existence.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 May 7;22(9):4984. doi: 10.3390/ijms22094984. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34067156 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Crucial Role of Extracellular Vesicles in Bronchial Asthma.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 May 27;20(10):2589. doi: 10.3390/ijms20102589. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31137771 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
From mesenchymal stem cells to their extracellular vesicles: Progress and prospects for asthma therapy.Asian J Pharm Sci. 2024 Aug;19(4):100942. doi: 10.1016/j.ajps.2024.100942. Epub 2024 Jul 9. Asian J Pharm Sci. 2024. PMID: 39253613 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nontargeted Toxicological/Chemical Analysis in Complex Mixtures for Risk Assessment and Key Driver Discovery.Environ Health (Wash). 2025 Mar 27;3(7):701-704. doi: 10.1021/envhealth.5c00052. eCollection 2025 Jul 18. Environ Health (Wash). 2025. PMID: 40704078 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
MiR-23a-5p alleviates chronic obstructive pulmonary disease through targeted regulation of RAGE-ROS pathway.Respir Res. 2024 Feb 20;25(1):93. doi: 10.1186/s12931-024-02736-y. Respir Res. 2024. PMID: 38378600 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular Vesicle microRNA: A Promising Biomarker and Therapeutic Target for Respiratory Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 23;25(17):9147. doi: 10.3390/ijms25179147. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39273095 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Blood-Based Biomarkers for Eosinophilic Esophagitis and Concomitant Atopic Diseases: A Look into the Potential of Extracellular Vesicles.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 11;24(4):3669. doi: 10.3390/ijms24043669. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36835081 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
