Role of oxidative stress versus lipids in monocrotaline-induced pulmonary hypertension and right heart failure
- PMID: 34816616
- PMCID: PMC8611258
- DOI: 10.14814/phy2.15090
Role of oxidative stress versus lipids in monocrotaline-induced pulmonary hypertension and right heart failure
Abstract
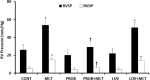
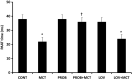
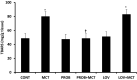
Pulmonary hypertension (PH) is a global health issue with a prevalence of 10% in ages >65 years. Right heart failure (RHF) is the main cause of death in PH. We have previously shown that monocrotaline (MCT)-induced PH and RHF are due to an increase in oxidative stress. In this study, probucol (PROB), a strong antioxidant with a lipid-lowering property, versus lovastatin (LOV), a strong lipid-lowering drug with some antioxidant effects, were evaluated for their effects on the MCT-induced RHF. Rats were treated (I.P.) with PROB (10 mg/kg ×12) or LOV (4 mg/kg ×12), daily 6 days before and 6 days after a single MCT injection (60 mg/kg). Serial echocardiography was performed and at 4-week post-MCT, lung wet-to-dry weight, hemodynamics, RV glutathione peroxidase (GSHPx), superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase, lipid peroxidation, and myocardial as well as plasma lipids were examined. MCT increased RV systolic and diastolic pressures, wall thickness, RV end diastolic diameter, mortality, and decreased ejection fraction as well as pulmonary artery acceleration time. These changes were mitigated by PROB while LOV had no effect. Furthermore, PROB prevented lipid peroxidation, lowered lipids, and increased GSHPx and SOD in RV myocardium. LOV did decrease the lipids but had no effect on antioxidants and lipid peroxidation. A reduction in oxidative stress and not the lipid-lowering effect of PROB may explain the prevention of MCT-induced PH, RHF, and mortality. Thus targeting of oxidative stress as an adjuvant therapy is suggested.
Keywords: antioxidants; oxidative stress; pulmonary hypertension; right heart failure.
© 2021 The Authors. Physiological Reports published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of The Physiological Society and the American Physiological Society.
Conflict of interest statement
There is no conflict of interest and no relationship with industry to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Antioxidant and oxidative stress changes in experimental cor pulmonale.Mol Cell Biochem. 2004 May;260(1-2):21-9. doi: 10.1023/b:mcbi.0000026047.48534.50. Mol Cell Biochem. 2004. PMID: 15228082
-
Beneficial effects of aqueous extract of stem bark of Terminalia arjuna (Roxb.), An ayurvedic drug in experimental pulmonary hypertension.J Ethnopharmacol. 2017 Feb 2;197:184-194. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2016.07.029. Epub 2016 Jul 9. J Ethnopharmacol. 2017. PMID: 27401289
-
Effects of afterload-reducing drugs on pathogenesis of antioxidant changes and congestive heart failure in rats.J Am Coll Cardiol. 1997 Mar 15;29(4):856-61. doi: 10.1016/s0735-1097(96)00574-8. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1997. PMID: 9091534
-
Effect of free and nanoemulsified β-caryophyllene on monocrotaline-induced pulmonary arterial hypertension.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2024 Apr;1871(4):119704. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2024.119704. Epub 2024 Mar 8. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2024. PMID: 38462075 Review.
-
PTEN as a Therapeutic Target in Pulmonary Hypertension Secondary to Left-heart Failure: Effect of HO-3867 and Supplemental Oxygenation.Cell Biochem Biophys. 2021 Sep;79(3):593-607. doi: 10.1007/s12013-021-01010-y. Epub 2021 Jun 16. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2021. PMID: 34133009 Review.
Cited by
-
The siRNA-mediated knockdown of AP-1 restores the function of the pulmonary artery and the right ventricle by reducing perivascular and interstitial fibrosis and key molecular players in cardiopulmonary disease.J Transl Med. 2024 Feb 5;22(1):137. doi: 10.1186/s12967-024-04933-1. J Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 38317144 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondrial fission produces a Warburg effect via the oxidative inhibition of prolyl hydroxylase domain-2.Redox Biol. 2025 Apr;81:103529. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2025.103529. Epub 2025 Feb 4. Redox Biol. 2025. PMID: 39978304 Free PMC article.
-
Probucol will become a new model for treating cerebral infarction with a high risk of hemorrhage: A narrative review.Brain Circ. 2023 Nov 30;9(4):222-227. doi: 10.4103/bc.bc_44_23. eCollection 2023 Oct-Dec. Brain Circ. 2023. PMID: 38284116 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Melatonin Improves Quality of Life, Oxidative Stress, and Cardiovascular Function in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension.Pulm Circ. 2025 Jun 19;15(2):e70109. doi: 10.1002/pul2.70109. eCollection 2025 Apr. Pulm Circ. 2025. PMID: 40538465 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akolkar, G. , da Silva, D. D. , Ayyappan, P. , Bagchi, A. K. , Jassal, D. S. , Salemi, V. M. C. , Irigoyen, M. C. , De Angelis, K. , & Singal, P. K. (2017). Vitamin C mitigates oxidative/nitrosative stress and inflammation in doxorubicin‐induced cardiomyopathy. American Journal of Physiology. Heart and Circulatory Physiology, 313, 795–809. 10.1152/ajpheart.00253.2017 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Aziz, S. M. , Toborek, M. , Hennig, B. , Mattson, M. P. , Guo, H. , & Lipke, D. W. (1997). Oxidative Stress mediates monocrotaline‐induced alterations in tenascin expression in pulmonary artery endothelial cells. International Journal of Biochemistry & Cell Biology, 29, 775–787. 10.1016/s1357-2725(97)00010-1 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bräsen, J. H. , Koenig, K. , Bach, H. , Kontush, A. , Heinle, H. , Witting, P. K. , Ylä‐Herttuala, S. , Stocker, R. , & Beisiegel, U. (2002). Comparison of the effects of alpha‐tocopherol, ubiquinone‐10 and probucol at therapeutic doses on atherosclerosis in WHHL rabbits. Atherosclerosis, 163(2), 249–259. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9150(02)00023-0 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Clairborne, A. (1985). Catalase activity. In Greenwald R. A. (Ed.), Handbook of methods for oxygen radical research (pp. 243–247). CRC Press.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

