Recurrence of atrial fibrillation after pulmonary vein isolation in dependence of arterial stiffness
- PMID: 34817833
- PMCID: PMC8941046
- DOI: 10.1007/s12471-021-01644-w
Recurrence of atrial fibrillation after pulmonary vein isolation in dependence of arterial stiffness
Abstract
Background: Arterial stiffness (AS) has emerged as a strong predictor of cardiovascular (CV) diseases. Although increased AS has been described as a predictor of atrial fibrillation (AF), its role as a risk marker for AF recurrence has not yet been elucidated.
Methods: Patients with AF who underwent pulmonary vein isolation (PVI) were included in this study. Presence of AS was evaluated by measuring aortic distensibility (AD) of the descending aorta by transoesophageal echocardiography.
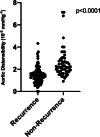
Results: In total, 151 patients (mean ± standard deviation (SD) age 71.9 ± 9.8 years) were enrolled and followed for a median duration of 21 months (interquartile range 15.0-31.0). During follow-up, AF recurred in 94 (62.3%) patients. AF recurrence was seen more frequently in patients with permanent AF (27% vs 46%, p = 0.03) and in those who had undergone prior PVI (9% vs 23%, p = 0.02). AD was significantly reduced in patients with AF recurrence (mean ± SD 2.6 ± 2.3 vs 1.5 ± 0.7 × 10-3 mm Hg-1, p < 0.0001), as well as left atrial volume index (LAVI) (mean ± SD 29 ± 12 vs 44 ± 15 ml/m2, p < 0.0001). Multivariable analysis revealed LAVI (odds ratio (OR) 2.9, 95% confidence interval (CI) 1.2-3.4) and AS (OR 3.6, 95% CI 2.8-4.1) as independent risk factors of AF recurrence.
Conclusion: Increased AS and left atrial size were independent predictors of AF recurrence after PVI. AD as surrogate marker of AS seemed to reflect the overall CV risk. In addition, AD was significantly correlated with left atrial size, which suggests that increased AS leads to atrial remodelling and thus to AF recurrence.
Trial registration: German registry for clinical studies (DRKS), DRKS00019007.
Keywords: Arterial stiffness; Atrial fibrillation; Left atrial volume index; Recurrence.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
T. Shchetynska-Marinova, M. Kranert, S. Baumann, V. Liebe, A. Grafen, S. Gerhards, S. Rosenkaimer, I. Akin, M. Borggrefe and A.L. Hohneck declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Kannel WB, Wolf PA, Benjamin EJ, Levy D. Prevalence, incidence, prognosis, and predisposing conditions for atrial fibrillation: population-based estimates 1. Am. J. Cardiol. 1998;82:2N–9N. - PubMed
-
- Heeringa J, van der Kuip DA, Hofman A, et al. Prevalence, incidence and lifetime risk of atrial fibrillation: the Rotterdam study. Eur Heart J. 2006;27:949–953. - PubMed
-
- Balk EM, Garlitski AC, Alsheikh-Ali AA, Terasawa T, Chung M, Ip S. Predictors of atrial fibrillation recurrence after radiofrequency catheter ablation: a systematic review. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2010;21:1208–1216. - PubMed
-
- Zhuang J, Wang Y, Tang K, et al. Association between left atrial size and atrial fibrillation recurrence after single circumferential pulmonary vein isolation: a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Europace. 2012;14:638–645. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials