Enterococcal bacteremia in mice is prevented by oral administration of probiotic Bacillus spores
- PMID: 34818053
- PMCID: PMC11097119
- DOI: 10.1126/scitranslmed.abf4692
Enterococcal bacteremia in mice is prevented by oral administration of probiotic Bacillus spores
Abstract
Whether and how probiotics promote human health is a controversial issue. Their claimed benefit for counteracting gastrointestinal infection is linked predominantly to reducing pathogen abundance within the intestinal microbiota. Less understood mechanistically is the reported value that probiotics could have in reducing systemic infections. Enterococcus faecalis is an opportunistic pathogen that causes systemic infection after translocation through the intestinal epithelium, particularly in hospitalized and immune-depleted patients receiving antibiotic therapy. In this study, we used an E. faecalis mouse infection model with wild-type and isogenic mutant strains deficient in genes of the E. faecalis Fsr (fecal streptococci regulator) quorum-sensing system. We show that E. faecalis translocation from the mouse gut into the blood is mediated by the Fsr quorum-sensing system through production of the protease GelE, which compromises intestinal epithelium integrity. Furthermore, we demonstrate that orally administered probiotic Bacillus subtilis spores blocked E. faecalis translocation from the gut to the bloodstream and subsequent systemic infection in mice by inhibiting Fsr activity. These findings demonstrate that a key aspect of Enterococcus pathogenesis is controlled by quorum sensing, which can be targeted with probiotic Bacillus spores.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
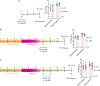
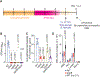
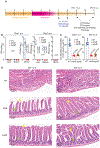
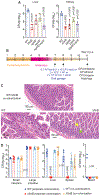




References
-
- Sanders ME, Merenstein DJ, Reid G, Gibson GR, Rastall RA, Probiotics and prebiotics in intestinal health and disease: from biology to the clinic. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 16, 605–616 (2019). - PubMed
-
- Saxelin M, Tynkkynen S, Mattila-Sandholm T, de Vos WM, Probiotic and other functional microbes: from markets to mechanisms. Curr Opin Biotechnol 16, 204–211 (2005). - PubMed
-
- van Baarlen P, Wells JM, Kleerebezem M, Regulation of intestinal homeostasis and immunity with probiotic lactobacilli. Trends Immunol 34, 208–215 (2013). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

