Feedback Loop Regulation between Pim Kinases and Tax Keeps Human T-Cell Leukemia Virus Type 1 Viral Replication in Check
- PMID: 34818069
- PMCID: PMC8826812
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.01960-21
Feedback Loop Regulation between Pim Kinases and Tax Keeps Human T-Cell Leukemia Virus Type 1 Viral Replication in Check
Abstract
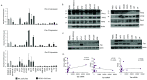
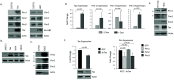
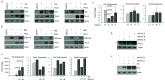
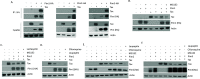
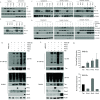
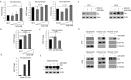
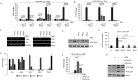
The Pim family of serine/threonine kinases promote tumorigenesis by enhancing cell survival and inhibiting apoptosis. Three isoforms exist, Pim-1, -2, and -3, that are highly expressed in hematological cancers, including Pim-1 in adult T-cell leukemia (ATL). Human T-cell leukemia virus type-1 (HTLV-1) is the etiological agent of ATL, a dismal lymphoproliferative disease known as adult T-cell leukemia. The HTLV-1 virally encoded oncogene Tax promotes CD4+ T-cell transformation through disruption of DNA repair pathways and activation of survival and cellular proliferation pathways. In this study, we found Tax increases the expression of Pim-1 and Pim-3, while decreasing Pim-2 expression. Furthermore, we discovered that Pim-1, -2, and -3 bind Tax protein to reduce its expression thereby creating a feedback regulatory loop between these two oncogenes. The loss of Tax expression triggered by Pim kinases led to loss in Tax-mediated transactivation of the HTLV-1 long terminal repeat (LTR) and reductions in HTLV-1 virus replication. Because Tax is also the immunodominant cytotoxic T cell lymphocytes (CTL) target, our data suggest that Pim kinases may play an important role in immune escape of HTLV-1-infected cells. IMPORTANCE The Pim family of protein kinases have established pro-oncogenic functions. They are often upregulated in cancer; especially leukemias and lymphomas. In addition, a role for Pim kinases in control of virus expression and viral latency is important for Kaposi sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV) and human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1). Our data demonstrate that HTLV-1 encodes viral genes that promote and maintain Pim kinase activation, which in turn may stimulate T-cell transformation and maintain ATL leukemic cell growth. HTLV-1 Tax increases expression of Pim-1 and Pim-3, while decreasing expression of Pim-2. In ATL cells, Pim expression is maintained through extended protein half-life and heat shock protection. In addition, we found that Pim kinases have a new role during HTLV-1 infection. Pim-1, -2, and -3 can subvert Tax expression and HTLV-1 virus production. This may lead to partial suppression of the host immunogenic responses to Tax and favor immune escape of HTLV-1-infected cells. Therefore, Pim kinases have not only pro-oncogenic roles but also favor persistence of the virus-infected cell.
Keywords: ATL; HBZ; Pim kinase; STAT signaling; Tax; human T-cell leukemia virus; leukemia; replication; transformation; virus.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Novel Interactions between the Human T-Cell Leukemia Virus Type 1 Antisense Protein HBZ and the SWI/SNF Chromatin Remodeling Family: Implications for Viral Life Cycle.J Virol. 2019 Jul 30;93(16):e00412-19. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00412-19. Print 2019 Aug 15. J Virol. 2019. PMID: 31142665 Free PMC article.
-
HSP90 protects the human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 (HTLV-1) tax oncoprotein from proteasomal degradation to support NF-κB activation and HTLV-1 replication.J Virol. 2013 Dec;87(24):13640-54. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02006-13. Epub 2013 Oct 9. J Virol. 2013. PMID: 24109220 Free PMC article.
-
Niclosamide, an anti-helminthic molecule, downregulates the retroviral oncoprotein Tax and pro-survival Bcl-2 proteins in HTLV-1-transformed T lymphocytes.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015 Aug 14;464(1):221-228. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2015.06.120. Epub 2015 Jun 23. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015. PMID: 26116531 Free PMC article.
-
HTLV-1 Infection and Adult T-Cell Leukemia/Lymphoma-A Tale of Two Proteins: Tax and HBZ.Viruses. 2016 Jun 16;8(6):161. doi: 10.3390/v8060161. Viruses. 2016. PMID: 27322308 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Adult T-cell leukemia-lymphoma as a viral disease: Subtypes based on viral aspects.Cancer Sci. 2021 May;112(5):1688-1694. doi: 10.1111/cas.14869. Epub 2021 Mar 30. Cancer Sci. 2021. PMID: 33630351 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Interplay between innate immunity and the viral oncoproteins Tax and HBZ in the pathogenesis and therapeutic response of HTLV-1 associated adult T cell leukemia.Front Immunol. 2022 Jul 22;13:957535. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.957535. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35935975 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Increased H19/miR-675 Expression in Adult T-Cell Leukemia Is Associated with a Unique Notch Signature Pathway.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 May 8;25(10):5130. doi: 10.3390/ijms25105130. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38791169 Free PMC article.
-
Trans-Activation of the Coactivator-Associated Arginine Methyltransferase 1 (Carm1) Gene by the Oncogene Product Tax of Human T-Cell Leukemia Virus Type 1.Genes (Basel). 2024 May 27;15(6):698. doi: 10.3390/genes15060698. Genes (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38927636 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting Pim kinases in hematological cancers: molecular and clinical review.Mol Cancer. 2023 Jan 25;22(1):18. doi: 10.1186/s12943-023-01721-1. Mol Cancer. 2023. PMID: 36694243 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Current State of Therapeutics for HTLV-1.Viruses. 2024 Oct 15;16(10):1616. doi: 10.3390/v16101616. Viruses. 2024. PMID: 39459949 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

