Risk for Stillbirth Among Women With and Without COVID-19 at Delivery Hospitalization - United States, March 2020-September 2021
- PMID: 34818318
- PMCID: PMC8612508
- DOI: 10.15585/mmwr.mm7047e1
Risk for Stillbirth Among Women With and Without COVID-19 at Delivery Hospitalization - United States, March 2020-September 2021
Abstract
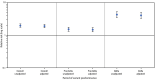
Pregnant women are at increased risk for severe COVID-19-related illness, and COVID-19 is associated with an increased risk for adverse pregnancy outcomes and maternal and neonatal complications (1-3). To date, studies assessing whether COVID-19 during pregnancy is associated with increased risk for stillbirth have yielded mixed results (2-4). Since the B.1.617.2 (Delta) variant of SARS-CoV-2 (the virus that causes COVID-19) became the predominant circulating variant,* there have been anecdotal reports of increasing rates of stillbirths in women with COVID-19.† CDC used the Premier Healthcare Database Special COVID-19 Release (PHD-SR), a large hospital-based administrative database,§ to assess whether a maternal COVID-19 diagnosis documented at delivery hospitalization was associated with stillbirth during March 2020-September 2021 as well as before and during the period of Delta variant predominance in the United States (March 2020-June 2021 and July-September 2021, respectively). Among 1,249,634 deliveries during March 2020-September 2021, stillbirths were rare (8,154; 0.65%): 273 (1.26%) occurred among 21,653 deliveries to women with COVID-19 documented at the delivery hospitalization, and 7,881 (0.64%) occurred among 1,227,981 deliveries without COVID-19. The adjusted risk for stillbirth was higher in deliveries with COVID-19 compared with deliveries without COVID-19 during March 2020-September 2021 (adjusted relative risk [aRR] = 1.90; 95% CI = 1.69-2.15), including during the pre-Delta (aRR = 1.47; 95% CI = 1.27-1.71) and Delta periods (aRR = 4.04; 95% CI = 3.28-4.97). COVID-19 documented at delivery was associated with increased risk for stillbirth, with a stronger association during the period of Delta variant predominance. Implementing evidence-based COVID-19 prevention strategies, including vaccination before or during pregnancy, is critical to reducing the impact of COVID-19 on stillbirths.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors have completed and submitted the International Committee of Medical Journal Editors form for disclosure of potential conflicts of interest. No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed.
Figures
References
-
- Zambrano LD, Ellington S, Strid P, et al. ; CDC COVID-19 Response Pregnancy and Infant Linked Outcomes Team. Update: characteristics of symptomatic women of reproductive age with laboratory-confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection by pregnancy status—United States, January 22–October 3, 2020. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2020;69:1641–7. 10.15585/mmwr.mm6944e3 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Allotey J, Stallings E, Bonet M, et al. ; for PregCOV-19 Living Systematic Review Consortium. Clinical manifestations, risk factors, and maternal and perinatal outcomes of coronavirus disease 2019 in pregnancy: living systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ 2020;370:m3320. 10.1136/bmj.m3320 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

