Lack of Hyperinhibition of Oriens Lacunosum-Moleculare Cells by Vasoactive Intestinal Peptide-Expressing Cells in a Model of Temporal Lobe Epilepsy
- PMID: 34819310
- PMCID: PMC8721516
- DOI: 10.1523/ENEURO.0299-21.2021
Lack of Hyperinhibition of Oriens Lacunosum-Moleculare Cells by Vasoactive Intestinal Peptide-Expressing Cells in a Model of Temporal Lobe Epilepsy
Abstract
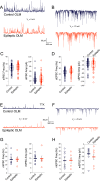
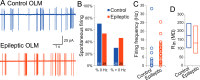
Temporal lobe epilepsy remains a common disorder with no cure and inadequate treatments, potentially because of an incomplete understanding of how seizures start. CA1 pyramidal cells and many inhibitory interneurons increase their firing rate in the seconds-minutes before a spontaneous seizure in epileptic rats. However, some interneurons fail to do so, including those identified as putative interneurons with somata in oriens and axons targeting lacunosum-moleculare (OLM cells). Somatostatin-containing cells, including OLM cells, are the primary target of inhibitory vasoactive intestinal polypeptide and calretinin-expressing (VIP/CR) bipolar interneuron-selective interneurons, type 3 (ISI-3). The objective of this study was to test the hypothesis that in epilepsy inhibition of OLM cells by ISI-3 is abnormally increased, potentially explaining the failure of OLM recruitment when needed most during the ramp up of activity preceding a seizure. Stereological quantification of VIP/CR cells in a model of temporal lobe epilepsy demonstrated that they survive in epileptic mice, despite a reduction in their somatostatin-expressing (Som) cell targets. Paired recordings of unitary IPSCs (uIPSCs) from ISI-3 to OLM cells did not show increased connection probability or increased connection strength, and failure rate was unchanged. When miniature postsynaptic currents in ISI-3 were compared, only mIPSC frequency was increased in epileptic hippocampi. Nevertheless, spontaneous and miniature postsynaptic potentials were unchanged in OLM cells of epileptic mice. These results are not consistent with the hypothesis of hyperinhibition from VIP/CR bipolar cells impeding recruitment of OLM cells in advance of a seizure.
Keywords: CA1; CCK; OLM; VIP; hippocampus; interneuron.
Copyright © 2021 Wyeth and Buckmaster.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Target-specific alterations in the VIP inhibitory drive to hippocampal GABAergic cells after status epilepticus.Exp Neurol. 2017 Jun;292:102-112. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2017.03.007. Epub 2017 Mar 15. Exp Neurol. 2017. PMID: 28315308
-
Dendritic inhibition provided by interneuron-specific cells controls the firing rate and timing of the hippocampal feedback inhibitory circuitry.J Neurosci. 2014 Mar 26;34(13):4534-47. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3813-13.2014. J Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 24671999 Free PMC article.
-
NMDA-Dependent Coplasticity in VIP Interneuron-Driven Inhibitory Circuits.J Neurochem. 2025 Jun;169(6):e70117. doi: 10.1111/jnc.70117. J Neurochem. 2025. PMID: 40522192
-
The vulnerability of calretinin-containing hippocampal interneurons to temporal lobe epilepsy.Front Neuroanat. 2014 Sep 29;8:100. doi: 10.3389/fnana.2014.00100. eCollection 2014. Front Neuroanat. 2014. PMID: 25324731 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cholinergic Modulation of Dendritic Signaling in Hippocampal GABAergic Inhibitory Interneurons.Neuroscience. 2022 May 1;489:44-56. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2021.06.011. Epub 2021 Jun 12. Neuroscience. 2022. PMID: 34129910 Review.
Cited by
-
Hyperexcitability: From Normal Fear to Pathological Anxiety and Trauma.Front Syst Neurosci. 2022 Aug 4;16:727054. doi: 10.3389/fnsys.2022.727054. eCollection 2022. Front Syst Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35993088 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impaired Response to Mismatch Novelty in the Li2+-Pilocarpine Rat Model of TLE: Correlation with Hippocampal Monoaminergic Inputs.Biomedicines. 2024 Mar 12;12(3):631. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12030631. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 38540244 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
