Radiotherapy as a tool to elicit clinically actionable signalling pathways in cancer
- PMID: 34819622
- PMCID: PMC9004227
- DOI: 10.1038/s41571-021-00579-w
Radiotherapy as a tool to elicit clinically actionable signalling pathways in cancer
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: Radiotherapy as a tool to elicit clinically actionable signalling pathways in cancer.Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2022 Apr;19(4):281. doi: 10.1038/s41571-022-00611-7. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35181748 No abstract available.
Abstract
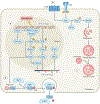
A variety of targeted anticancer agents have been successfully introduced into clinical practice, largely reflecting their ability to inhibit specific molecular alterations that are required for disease progression. However, not all malignant cells rely on such alterations to survive, proliferate, disseminate and/or evade anticancer immunity, implying that many tumours are intrinsically resistant to targeted therapies. Radiotherapy is well known for its ability to activate cytotoxic signalling pathways that ultimately promote the death of cancer cells, as well as numerous cytoprotective mechanisms that are elicited by cellular damage. Importantly, many cytoprotective mechanisms elicited by radiotherapy can be abrogated by targeted anticancer agents, suggesting that radiotherapy could be harnessed to enhance the clinical efficacy of these drugs. In this Review, we discuss preclinical and clinical data that introduce radiotherapy as a tool to elicit or amplify clinically actionable signalling pathways in patients with cancer.
© 2021. Springer Nature Limited.
Figures
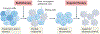
References
-
- Bedard PL, Hyman DM, Davids MS & Siu LL Small molecules, big impact: 20 years of targeted therapy in oncology. Lancet 395, 1078–1088 (2020). - PubMed
-
- Boumahdi S & de Sauvage FJ The great escape: tumour cell plasticity in resistance to targeted therapy. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov 19, 39–56 (2020). - PubMed
-
- Sotorasib edges closer to approval. Cancer Discov. 11, OF2 (2021). - PubMed
-
- Doroshow DB et al. PD-L1 as a biomarker of response to immune-checkpoint inhibitors. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol 18, 345–362 (2021). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

