The human microbiome encodes resistance to the antidiabetic drug acarbose
- PMID: 34819672
- PMCID: PMC10258454
- DOI: 10.1038/s41586-021-04091-0
The human microbiome encodes resistance to the antidiabetic drug acarbose
Abstract
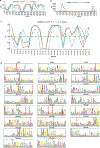
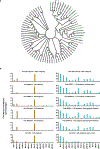
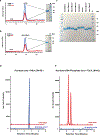
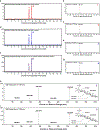
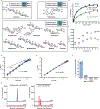
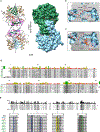
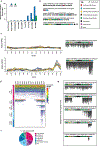
The human microbiome encodes a large repertoire of biochemical enzymes and pathways, most of which remain uncharacterized. Here, using a metagenomics-based search strategy, we discovered that bacterial members of the human gut and oral microbiome encode enzymes that selectively phosphorylate a clinically used antidiabetic drug, acarbose1,2, resulting in its inactivation. Acarbose is an inhibitor of both human and bacterial α-glucosidases3, limiting the ability of the target organism to metabolize complex carbohydrates. Using biochemical assays, X-ray crystallography and metagenomic analyses, we show that microbiome-derived acarbose kinases are specific for acarbose, provide their harbouring organism with a protective advantage against the activity of acarbose, and are widespread in the microbiomes of western and non-western human populations. These results provide an example of widespread microbiome resistance to a non-antibiotic drug, and suggest that acarbose resistance has disseminated in the human microbiome as a defensive strategy against a potential endogenous producer of a closely related molecule.
© 2021. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



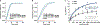
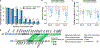
References
-
- Chiasson JL et al. Acarbose for prevention of type 2 diabetes mellitus: the STOP-NIDDM randomised trial. Lancet 359, 2072–2077 (2002). - PubMed
-
- Wehmeier UF & Piepersberg W Biotechnology and molecular biology of the alpha-glucosidase inhibitor acarbose. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 63, 613–625 (2004). - PubMed
-
- Yoon S-H & Robyt JF Study of the inhibition of four alpha amylases by acarbose and its 4IV-α-maltohexaosyl and 4IV-α-maltododecaosyl analogues. Carbohydr. Res. 338, 1969–1980 (2003). - PubMed
-
- Wu H et al. Metformin alters the gut microbiome of individuals with treatment–naive type 2 diabetes, contributing to the therapeutic effects of the drug. Nat. Med. 23, 850–858 (2017). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

