Baicalin Enhanced Oral Bioavailability of Sorafenib in Rats by Inducing Intestine Absorption
- PMID: 34819863
- PMCID: PMC8606670
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2021.761763
Baicalin Enhanced Oral Bioavailability of Sorafenib in Rats by Inducing Intestine Absorption
Abstract
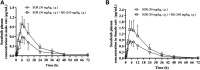
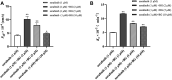
Background: Sorafenib (SOR) is an oral, potent, selective, irreversible epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor (EGFR-TKI) used as the first-line therapy for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Baicalin (BG) is used as adjuvant therapy for hepatitis, which accounts for the leading cause of the development of HCC, and is commonly coadministered with SOR in clinic. The purpose of the current study was to characterize the pharmacokinetic changes of SOR and the potential mechanism when SOR is administered concomitantly with BG in rats for single and multiple doses. Methods: Parallel randomized pharmacokinetic studies were performed in rats which received SOR (50 mg/kg, i.g.) alone or coadministered with BG (160 mg/kg, i.g.) for single and multiple doses (7 days). Plasma SOR levels were quantified by ultra-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (UPLC-MS/MS). Rat liver microsomes (RLMs) which isolated from their livers were analyzed for CYP3A and SOR metabolism activities. The inhibitory effect of BG on the metabolism of SOR was also assessed in pooled human liver microsomes (HLMs). The effects of BG on the intestine absorption behaviors of SOR were assessed in the in situ single-pass rat intestinal perfusion model. Results: Coadministration with BG (160 mg/kg, i.g.) for single or multiple doses significantly increased the Cmax, AUC0-t, and AUC0-∞ of orally administered SOR by 1.68-, 1.73-, 1.70-fold and 2.02-, 1.65-, 1.66- fold in male rats and by 1.85-, 1.68-, 1.68-fold and 1.57-, 1.25-, 1.24- fold in female rats, respectively (p < 0.01 or p < 0.05). In vitro incubation assays demonstrated that there were no significant differences of K m , V max , and CL int of 1-OH MDZ and SOR N-oxide in RLMs between control and multiple doses of BG-treated groups. BG has no obvious inhibitory effects on the metabolism of SOR in HLMs. In comparison with SOR alone, combining with BG significantly increased the permeability coefficient (P eff ) and absorption rate constant (K a ) of the SOR in situ single-pass rat intestinal perfusion model. Conclusion: Notably enhanced oral bioavailability of SOR by combination with BG in rats may mainly account for BG-induced SOR absorption. A greater understanding of potential DDIs between BG and SOR in rats makes major contributions to clinical rational multidrug therapy in HCC patients. Clinical trials in humans and HCC patients need to be further confirmed in the subsequent study.
Keywords: baicalin; bioavailability; drug–drug interactions; in situ single-pass rat intestinal perfusion model; sorafenib.
Copyright © 2021 Wei, Liu, Zhang, Liu, Yan, Wen and Tian.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


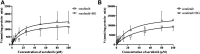

References
-
- Awada A., Hendlisz A., Christensen O., Lathia C. D., Bartholomeus S., Lebrun F., et al. (2012). Phase I Trial to Investigate the Safety, Pharmacokinetics and Efficacy of Sorafenib Combined with Docetaxel in Patients with Advanced Refractory Solid Tumours. Eur. J. Cancer 48 (4), 465–474. 10.1016/j.ejca.2011.12.026 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

