Multiple Risk Factors for Heart Disease: A Challenge to the Ethnopharmacological Use of Croton urucurana Baill
- PMID: 34819983
- PMCID: PMC8608512
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/6580458
Multiple Risk Factors for Heart Disease: A Challenge to the Ethnopharmacological Use of Croton urucurana Baill
Abstract
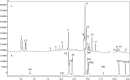
Croton urucurana Baill. is a native Brazilian tree, popularly known as "sangra-d'água" or "sangue-de-dragão," based on the red resinous sap of the trunk. Its use has been transmitted through generations based on popular tradition that attributes analgesic, anti-inflammatory, and cardioprotective properties to the tree. However, its cardioprotective effects have not yet been scientifically investigated. Thus, the present study investigated the pharmacological response to an ethanol-soluble fraction from the leaves of C. urucurana in Wistar rats exposed to smoking and dyslipidemia, two important cardiovascular risk factors. The extract was evaluated by high-performance liquid chromatography. Wistar rats received a 0.5% cholesterol-enriched diet and were exposed to cigarette smoke (9 cigarettes/day for 10 weeks). During the last 5 weeks, the animals were orally treated with vehicle (negative control group), C. urucurana extract (30, 100, and 300 mg/kg), or simvastatin (2.5 mg/kg) + enalapril (15 mg/kg). One group of rats that was not exposed to these risk factors was also evaluated (basal group). Electrocardiograms and systolic, diastolic, and mean blood pressure were measured. Blood was collected to measure total cholesterol, triglycerides, urea, and creatinine. The heart and kidneys were collected and processed for oxidative status and histopathological evaluation. The phytochemical analysis revealed different classes of flavonoids and condensed tannins. The model induced dyslipidemia and cardiac and renal oxidative stress and increased levels of urea and creatinine in the negative control group. Treatment with the C. urucurana extract (300 mg/kg) and simvastatin + enalapril decreased cholesterol and triglyceride levels. In contrast to simvastatin + enalapril treatment, the C. urucurana extract exerted cardiac and renal antioxidant effects. No alterations of electrocardiograms, blood pressure, or histopathology were observed between groups. These findings indicate that C. urucurana exerts lipid-lowering, renal, and cardioprotective effects against oxidative stress in a preclinical model of multiple risk factors for heart disease.
Copyright © 2021 Priscila Megda João Job Zago et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest related to this research.
Figures



References
-
- Balwan W. K., Kour S. Lifestyle diseases: the link between modern lifestyle and threat to public health. Saudi Journal of Medical and Pharmaceutical Sciences . 2021;7(4):179–184. doi: 10.36348/sjmps.2021.v07i04.00X. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

