Efficacy of targeted therapy in patients with HER2-positive non-small cell lung cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 34820879
- PMCID: PMC9302639
- DOI: 10.1111/bcp.15155
Efficacy of targeted therapy in patients with HER2-positive non-small cell lung cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
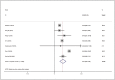
Anti-human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) therapy is an effective treatment for HER2-positive gastric and breast malignancies. However, the efficacy of HER2-targeted therapy in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients with HER2 alterations remains controversial. We searched studies on HER2-targeted therapy in NSCLC patients that reported objective response rate (ORR), disease control rate (DCR) and progressionfree survival (PFS) published from database inception to 30 May 2021. A total of 32 trials involving 958 patients were included. The ORRs of HER2-TKIs targeted therapy, humanised monoclonal antibody, trastuzumab-based treatment and antibody-drug conjugate (ADC) (T-DM1) were 22% (95% CI 11-31), 23% (95% CI 20-65), 26% (95% CI 14-39) and 16% (95% CI _6-37), while that of ADC (DS-8201) was 60% (95% CI 35-85). The DCRs of these groups were 59% (95% CI 49-69), 39% (95% CI _9-88), 63% (95% CI 37-89), 31% (95% CI 4-58) and 87% (95% CI 62-112), respectively. In the subgroup analysis, numerically higher ORRs and DCRs were observed in the poziotinib (38%; 75%) and pyrotinib (35%; 83%) groups. The median PFSs of these groups were 5.51 months, 3.09 months, 4.61 months, 2.65 months and 12.04 months, respectively. HER2-targeted therapy can be considered an acceptable treatment strategy for NSCLC patients with HER2 alterations. In particular, ADC (DS-8201), pyrotinib and poziotinib demonstrated promising anti-tumour activity in HER2-positive NSCLC.
Keywords: ERBB2; HER2; biomarkers; meta-analysis; non-small cell lung cancer; review; targeted therapy.
© 2021 The Authors. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of British Pharmacological Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
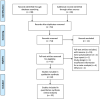
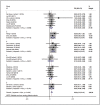

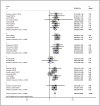
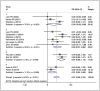

References
-
- Kalemkerian GP, Narula N, Kennedy EB, et al. Molecular testing guideline for the selection of patients with lung cancer for treatment with targeted tyrosine kinase inhibitors: American Society of Clinical Oncology endorsement of the College of American Pathologists/International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer/Association for Molecular Pathology Clinical Practice guideline update. J Clin Oncol. 2018;36(9):911‐919. 10.1200/JCO.2017.76.7293 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

