Microparticle-tagged image-based cell counting (ImmunoSpin) for CD4 + T cells
- PMID: 34822013
- PMCID: PMC8616869
- DOI: 10.1007/s00604-021-05070-y
Microparticle-tagged image-based cell counting (ImmunoSpin) for CD4 + T cells
Abstract
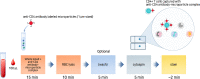
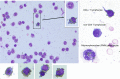
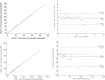
Affordable point-of-care (POC) CD4 + T lymphocyte counting techniques have been developed as alternatives to flow cytometry-based instruments caring for patients with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-1. However, POC CD4 enumeration technologies can be inaccurate. Here, we developed a microparticle-based visual detector of CD4 + T lymphocytes (ImmunoSpin) using microparticles conjugated with anti-CD4 antibodies, independent of microfluidic or fluorescence detection systems. Visual enumeration of CD4 + T cells under conventional light microscope was accurate compared to flow cytometry. Microparticle-tagged CD4 + T cells were well-recognized under a light microscope. ImmunoSpin showed very good precision (coefficients of variation of ImmunoSpin were ≤ 10%) and high correlation with clinical-grade flow cytometry for the enumeration of CD4 + T cells (y = 0.4232 + 0.9485 × for the %CD4 + T cell count, R2 = 0.99). At thresholds of 200 and 350 cells/µL, there was no misclassification of the ImmunoSpin system compared to the reference flow cytometry. ImmunoSpin showed clear differential classification of CD4 + T lymphocytes from granulocytes and monocytes. Because non-fluorescence microparticle-tags and cytospin slides are used in ImmunoSpin, they can be applied to an automatic digital image analyzer. Slide preparation allows long-term storage, no analysis time limitations, and image transfer in remote areas.
Keywords: CD4 + T cell; Human immunodeficiency virus; Image-based cell counting; ImmunoSpin; Microparticle.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Performance of the BD FACSPresto near to patient analyzer in comparison with representative conventional CD4 instruments in Cameroon.AIDS Res Ther. 2020 Aug 17;17(1):53. doi: 10.1186/s12981-020-00309-9. AIDS Res Ther. 2020. PMID: 32799909 Free PMC article.
-
Thirty-five years of CD4 T-cell counting in HIV infection: From flow cytometry in the lab to point-of-care testing in the field.Cytometry B Clin Cytom. 2017 Nov;92(6):437-444. doi: 10.1002/cyto.b.21400. Epub 2016 Aug 3. Cytometry B Clin Cytom. 2017. PMID: 27406947 Review.
-
Near patient CD4 count in a hospitalized HIV patient population.Cytometry B Clin Cytom. 2017 Nov;92(6):451-455. doi: 10.1002/cyto.b.21248. Epub 2015 May 27. Cytometry B Clin Cytom. 2017. PMID: 25917935 Free PMC article.
-
CD4+ T lymphocytes enumeration by an easy-to-use single platform image cytometer for HIV monitoring in resource-constrained settings.Cytometry B Clin Cytom. 2007 Sep;72(5):397-407. doi: 10.1002/cyto.b.20165. Cytometry B Clin Cytom. 2007. PMID: 17311352
-
Evaluation of a flow cytometry method for CD4 T cell enumeration based on volumetric primary CD4 gating using thermoresistant reagents.J Immunol Methods. 2011 Sep 30;372(1-2):7-13. doi: 10.1016/j.jim.2011.07.012. Epub 2011 Jul 29. J Immunol Methods. 2011. PMID: 21835181 Review.
Cited by
-
Artificial intelligence-enabled microfluidic cytometer using gravity-driven slug flow for rapid CD4+ T cell quantification in whole blood.Microsyst Nanoeng. 2025 Feb 28;11(1):36. doi: 10.1038/s41378-025-00881-y. Microsyst Nanoeng. 2025. PMID: 40016189 Free PMC article.
-
Microfluidic Assays for CD4 T Lymphocyte Counting: A Review.Biosensors (Basel). 2025 Jan 9;15(1):33. doi: 10.3390/bios15010033. Biosensors (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39852084 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kestens L, Mandy F. Thirty-five years of CD4 T-cell counting in HIV infection: from flow cytometry in the lab to point-of-care testing in the field. Cytometry B Clin Cytom. 2017;92:437–444. - PubMed
-
- Shafiee H, Wang S, Inci F, Toy M, Henrich TJ, et al. Emerging technologies for point-of-care management of HIV infection. Annu Rev Med. 2015;66:387–405. - PubMed
-
- Gondhalekar C, Rajwa B, Patsekin V, Ragheb K, Sturgis J, et al. Alternatives to current flow cytometry data analysis for clinical and research studies. Methods. 2018;134–135:113–129. - PubMed
-
- Degandt S, Peeters B, Jughmans S, Boeckx N, Bossuyt X. Analytical performance of an automated volumetric flow cytometer for quantitation of T, B and natural killer lymphocytes. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2018;56:1277–1288. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
