Botulinum Neurotoxin Type A in the Treatment of Facial Seborrhea and Acne: Evidence and a Proposed Mechanism
- PMID: 34822601
- PMCID: PMC8626011
- DOI: 10.3390/toxins13110817
Botulinum Neurotoxin Type A in the Treatment of Facial Seborrhea and Acne: Evidence and a Proposed Mechanism
Abstract
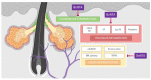
Intradermal injection of botulinum neurotoxin is a frequently performed procedure in aesthetic dermatology to improve facial skin tone, texture, fine wrinkles, and enlarged pores. In practice, botulinum neurotoxin type A is also used to reduce skin oiliness of the face. There is increasing evidence that acetylcholine plays specific roles in sebum production, suggesting that botulinum neurotoxin type A may reduce sebum production by interfering with cholinergic transmission between sebaceous glands and autonomic nerve terminals. Botulinum neurotoxins can also inhibit several pathogenetic components of acne development, suggesting that botulinum neurotoxins can be used as a safe and effective treatment modality for acne and other skin disorders related to overactivity of sebaceous glands. This review aims to explore the current evidence behind the treatment of facial seborrhea and acne with botulinum neurotoxin type A.
Keywords: acetylcholine; acne vulgaris; botulinum toxins; cholinergic receptors; non-neuronal cholinergic system; oily skin; sebaceous glands; seborrhea; sebum.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Arbuckle R., Atkinson M.J., Clark M., Abetz L., Lohs J., Kuhagen I., Harness J., Draelos Z., Thiboutot D., Blume-Peytavi U., et al. Patient experiences with oily skin: The qualitative development of content for two new patient reported outcome questionnaires. Health Qual. Life Outcomes. 2008;6:1–15. doi: 10.1186/1477-7525-6-80. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

