The allergy mediator histamine confers resistance to immunotherapy in cancer patients via activation of the macrophage histamine receptor H1
- PMID: 34822775
- PMCID: PMC8779329
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ccell.2021.11.002
The allergy mediator histamine confers resistance to immunotherapy in cancer patients via activation of the macrophage histamine receptor H1
Abstract
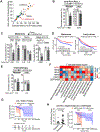
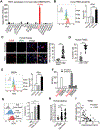
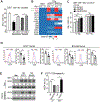
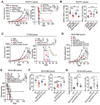
Reinvigoration of antitumor immunity remains an unmet challenge. Our retrospective analyses revealed that cancer patients who took antihistamines during immunotherapy treatment had significantly improved survival. We uncovered that histamine and histamine receptor H1 (HRH1) are frequently increased in the tumor microenvironment and induce T cell dysfunction. Mechanistically, HRH1-activated macrophages polarize toward an M2-like immunosuppressive phenotype with increased expression of the immune checkpoint VISTA, rendering T cells dysfunctional. HRH1 knockout or antihistamine treatment reverted macrophage immunosuppression, revitalized T cell cytotoxic function, and restored immunotherapy response. Allergy, via the histamine-HRH1 axis, facilitated tumor growth and induced immunotherapy resistance in mice and humans. Importantly, cancer patients with low plasma histamine levels had a more than tripled objective response rate to anti-PD-1 treatment compared with patients with high plasma histamine. Altogether, pre-existing allergy or high histamine levels in cancer patients can dampen immunotherapy responses and warrant prospectively exploring antihistamines as adjuvant agents for combinatorial immunotherapy.
Keywords: HRH1; T cell dysfunction; allergy; antihistamine; cancer immunotherapy; histamine; immune evasion; macrophage.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Comment in
-
Anti-histamines boost immunotherapy.Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2022 Jan;21(1):17. doi: 10.1038/d41573-021-00204-6. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2022. PMID: 34862488 No abstract available.
-
Antitumour roles for antihistamines.Nat Rev Immunol. 2022 Jan;22(1):4-5. doi: 10.1038/s41577-021-00670-4. Nat Rev Immunol. 2022. PMID: 34880394 No abstract available.
-
Antihistamines boost immunotherapy.Nat Rev Cancer. 2022 Feb;22(2):69. doi: 10.1038/s41568-021-00437-y. Nat Rev Cancer. 2022. PMID: 34903891 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

