From structure to clinic: Design of a muscarinic M1 receptor agonist with potential to treatment of Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 34822784
- PMCID: PMC7616177
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2021.11.001
From structure to clinic: Design of a muscarinic M1 receptor agonist with potential to treatment of Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
Current therapies for Alzheimer's disease seek to correct for defective cholinergic transmission by preventing the breakdown of acetylcholine through inhibition of acetylcholinesterase, these however have limited clinical efficacy. An alternative approach is to directly activate cholinergic receptors responsible for learning and memory. The M1-muscarinic acetylcholine (M1) receptor is the target of choice but has been hampered by adverse effects. Here we aimed to design the drug properties needed for a well-tolerated M1-agonist with the potential to alleviate cognitive loss by taking a stepwise translational approach from atomic structure, cell/tissue-based assays, evaluation in preclinical species, clinical safety testing, and finally establishing activity in memory centers in humans. Through this approach, we rationally designed the optimal properties, including selectivity and partial agonism, into HTL9936-a potential candidate for the treatment of memory loss in Alzheimer's disease. More broadly, this demonstrates a strategy for targeting difficult GPCR targets from structure to clinic.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; G protein coupled receptors; M1 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor; muscarinic receptor; neurodegeneration; prion disease; structural based drug design.
Copyright © 2021. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests T.T. and M.W. are shareholders and board members of Sosei Heptares. The authors A.J.H.B., G.A.B., K.A.B., J.B., J.E.C., M.S.C., R.M.C., J.C.E., E.H., A.J., C.J.L., J.L., F.H.M., P.J.N., K.O., G.O., J.C.P., M.P., N.R., P.R., B.G.T., R.T.S., C.d.G., G.M., and B.T. are or have been employees of Heptares Therapeutics and are shareholders of Sosei Heptares.
Figures
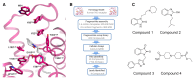
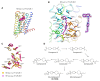

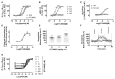
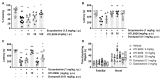
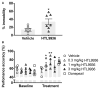
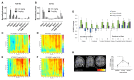
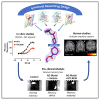
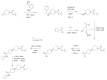
Comment in
-
Muscarinic receptors: from clinic to bench to clinic.Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2022 Jun;43(6):461-463. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2022.01.006. Epub 2022 Jan 31. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35101279 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alt A, Pendri A, Bertekap RL, Li G, Benitex Y, Nophsker M, Rockwell KL, Burford NT, Sum CS, Chen J, et al. Evidence for Classical Cholinergic Toxicity Associated with Selective Activation of M1 Muscarinic Receptors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2016;356:293–304. - PubMed
-
- Antonova E, Parslow D, Brammer M, Dawson GR, Jackson SH, Morris RG. Age-related neural activity during allocentric spatial memory. Memory. 2009;17:125–143. - PubMed
-
- Antonova E, Parslow D, Brammer M, Simmons A, Williams S, Dawson GR, Morris R. Scopolamine disrupts hippocampal activity during allocentric spatial memory in humans: an fMRI study using a virtual reality analogue of the Morris Water Maze. J Psychopharmacol. 2011;25:1256–1265. - PubMed
-
- Avlani VA, Langmead CJ, Guida E, Wood MD, Tehan BG, Herdon HJ, Watson JM, Sexton PM, Christopoulos A. Orthosteric and allosteric modes of interaction of novel selective agonists of the M1 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor. Mol Pharmacol. 2010;78:94–104. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

