LGI1 antibody encephalitis: acute treatment comparisons and outcome
- PMID: 34824144
- PMCID: PMC8862031
- DOI: 10.1136/jnnp-2021-327302
LGI1 antibody encephalitis: acute treatment comparisons and outcome
Abstract
Objective: To compare acute treatment responses and long-term outcome in leucine-rich glioma-inactivated 1 (LGI1) antibody encephalitis.
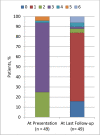
Methods: Retrospective case series of 118 patients with LGI1 antibody encephalitis evaluated at Mayo Clinic across all US sites from 1 May 2008 to 31 March 2019. Patient clinical data were identified and analysed through the neuroimmunology laboratory and electronic medical record. LGI1 antibody detection was by cell-based indirect immunofluorescence assay of serum, cerebrospinal fluid or both. Clinical outcomes were faciobrachial dystonic seizure (FBDS) resolution, modified Rankin Scale (mRS) score, Kokmen Short Test of Mental Status (STMS) score (0-38 point scale) and neuropsychometric testing results.
Results: Compared with intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIg) (n=21), patients treated with single-agent acute corticosteroids (intravenous, oral or both) (n=49) were more likely to experience resolution of FBDS (61% vs 7%, p=0.002) and improvements in mRS score (ΔmRS score 2 vs 0, p=0.008) and median Kokmen STMS scores (ΔKokmen STMS score 5 points vs 0 points, p=0.01). In 54 patients with long-term follow-up (≥2 years), the median mRS score was 1 (range 0-6) and the median Kokmen STMS score was 36 (range 24-38) after all combinations of immunotherapy. Neuropsychometric testing in 32 patients with long-term follow-up (≥2 years) demonstrated short-term memory impairments in 37%.
Conclusions: Corticosteroids appeared more effective acutely than IVIg in improving LGI1 antibody encephalitis in this retrospective comparison of immunotherapies. While improvement with immunotherapy is typical and long-term outcome is favourable, short-term memory deficits are noted in approximately a third of the patients.
Keywords: autoimmune encephalitis; neuroimmunology; steroids.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2022. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
Comment in
-
Improving clinical practice with an old friend from the neuroimmunology toolkit: acute corticosteroids in LGI1 antibody encephalitis.J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2022 Mar;93(3):230-231. doi: 10.1136/jnnp-2021-327643. Epub 2021 Nov 25. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2022. PMID: 34824145 No abstract available.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical