Upregulated type I interferon responses in asymptomatic COVID-19 infection are associated with improved clinical outcome
- PMID: 34824360
- PMCID: PMC8617268
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-02489-4
Upregulated type I interferon responses in asymptomatic COVID-19 infection are associated with improved clinical outcome
Abstract
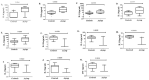
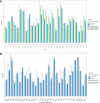
Understanding key host protective mechanisms against SARS-CoV-2 infection can help improve treatment modalities for COVID-19. We used a blood transcriptome approach to study biomarkers associated with differing severity of COVID-19, comparing severe and mild Symptomatic disease with Asymptomatic COVID-19 and uninfected Controls. There was suppression of antigen presentation but upregulation of inflammatory and viral mRNA translation associated pathways in Symptomatic as compared with Asymptomatic cases. In severe COVID-19, CD177 a neutrophil marker, was upregulated while interferon stimulated genes (ISGs) were downregulated. Asymptomatic COVID-19 cases displayed upregulation of ISGs and humoral response genes with downregulation of ICAM3 and TLR8. Compared across the COVID-19 disease spectrum, we found type I interferon (IFN) responses to be significantly upregulated (IFNAR2, IRF2BP1, IRF4, MAVS, SAMHD1, TRIM1), or downregulated (SOCS3, IRF2BP2, IRF2BPL) in Asymptomatic as compared with mild and severe COVID-19, with the dysregulation of an increasing number of ISGs associated with progressive disease. These data suggest that initial early responses against SARS-CoV-2 may be effectively controlled by ISGs. Therefore, we hypothesize that treatment with type I interferons in the early stage of COVID-19 may limit disease progression by limiting SARS-CoV-2 in the host.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
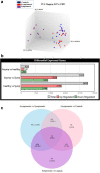
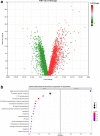
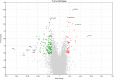
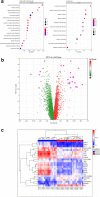
References
-
- JHU. COVID-19 Data Repository by the Center for Systems Science and Engineering (CSSE) at Johns Hopkins University. https://github.com/CSSEGISandData/COVID-19 (2021).
-
- Pakistan Bureau of Statistics . Social Indicators of Pakistan. Pakistan Bureau of Statistics; 2016.
-
- Government of Pakistan. COVID-19 Health Advisory Platform. Ministry of National Health Services Regulations and Coordination.https://covid.gov.pk/ (2021).
-
- Lai CC, et al. Global epidemiology of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): Disease incidence, daily cumulative index, mortality, and their association with country healthcare resources and economic status. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents. 2020;55:105946. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.105946. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

