QLF-D: A Contemporary Plaque Control Tool in Children
- PMID: 34824504
- PMCID: PMC8585893
- DOI: 10.5005/jp-journals-10005-2001
QLF-D: A Contemporary Plaque Control Tool in Children
Abstract
Background and objectives: The main causative factors for maximum periodontal diseases are dental plaque and oral biofilms. This study was done to check the impact of quantitative light-induced fluorescence-digital (QLF-D) as a motivational tool for plaque control among children from various schools situated in Dehradun district along with education using audiovisual aids.
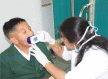
Materials and methods: A total sample of 800 school-going children including both males and females aged 6 to 12 years from various schools situated in Dehradun district of Uttarakhand were surveyed. A pro forma was prepared and the demographics of the students were noted. All the students were first examined for the Oral Hygiene Index-Simplified (OHI-S) and then the random division was done into two groups, group A (Q-scan) and group B (basic diagnostic aids) for examination of plaque index.
Results: The results of the study revealed that good OHI-S scores increased significantly from 1st visit to 3rd visit. The plaque scores for the control group, when examined with basic diagnostic aids of all three visits, were significantly good which increased subsequently from 1st visit to 3rd visit. Good plaque index score increased significantly for the test group from 1st to 3rd visit when examined with QLF-D.
Conclusion: We found in our study that QLF technology is of paramount importance in epidemiological surveys and plays a pivotal role in evaluating masses in maintaining oral health care.
How to cite this article: Solanki R, Tuli A, Dhawan P, et al. QLF-D: A Contemporary Plaque Control Tool in Children. Int J Clin Pediatr Dent 2021;14(4):502-505.
Keywords: Audiovisual aids; Dental plaque; Mechanical plaque control; Oral health education; Q-scan device.
Copyright © 2021; Jaypee Brothers Medical Publishers (P) Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Source of support: Nil Conflict of interest: None
Figures
References
-
- Mandal A, Singh DK, Siddiqui H, et al. New dimensions in mechanical plaque control: an overview. Indian J DentSci. 2017;9(2):133–139. doi: 10.4103/IJDS.IJDS_18_17. - DOI
-
- Ahad M, Gheena S. Awareness of tooth brushing techniques and proper oral hygiene among school children. J Pharmaceut Sci Res. 2015;7(6):367–372.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources