Comparison of Efficacy of Adductor Canal Block, Local Infiltration Analgesia and Both Combined in Postoperative Pain Management After Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Randomized Controlled Trial
- PMID: 34824710
- PMCID: PMC8586381
- DOI: 10.1007/s43465-021-00482-7
Comparison of Efficacy of Adductor Canal Block, Local Infiltration Analgesia and Both Combined in Postoperative Pain Management After Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Abstract
Purpose: The aim of our study is to compare the efficacy of adductor canal block (ACB), periarticular local infiltration (PLI) and both combined (ACB + PLI) in multimodal pain management after TKA.
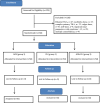
Methods: This is a prospective, randomized controlled double-blinded study undergoing primary unilateral TKA. They were randomized into three groups with fifty patients in each group: ACB alone (30 ml of 0.2% ropivacaine), PLI alone (30 ml 0.5% ropivacaine in 20 ml of normal saline), and both combined (ACB + PLI). The primary outcome studied was pain using visual analog score (VAS) in postoperative days (POD) 1 and 2. The secondary outcomes estimated were the ambulation capacity, the knee range of motion, need for rescue analgesia and length of hospital stay.
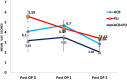
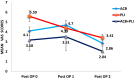
Results: The mean VAS score was significantly lower at rest and after mobilization in the combined group (3.51 at POD 1, 2.04 at POD 2), compared with either alone group (ACB = 4.70, 2.86 versus PLI = 4.39, 3.41 at POD 1 and 2 respectively after mobilization, p < 0.001). The ambulation capacity (combined = 103.3 steps versus ACB = 98.1 and PLI = 95.2 steps, p = 0.04) and the knee range of motion (arc of motion 106.7 degrees versus ACB = 104.9 and PLI = 102.2 degrees, p = 0.004) were significantly higher in the combined group compared to the other groups. There was no significant difference in the length of stay between the groups (p = 0.12).
Conclusion: Adductor canal block combined with periarticular local infiltration provides better pain relief, good range of motion, quicker rehabilitation, and reduced opioid consumption.
Keywords: Adductor canal block; Functional outcome; Pain; Periarticular local infiltration analgesia; Total knee arthroplasty.
© Indian Orthopaedics Association 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestNatesan Rajkumar, Manickam Karthikeyan, Dhanasekaran Soundarrajan, Palanisami Dhanasekararaja and Shanmuganathan Rajasekaran declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Kwofie MK, Shastri UD, Gadsden JC, et al. The effects of ultrasound-guided adductor canal block versus femoral nerve block on quadriceps strength and fall risk: a blinded, randomized trial of volunteers. Regional Anesthesia and Pain Medicine. 2013;38(4):321–325. doi: 10.1097/AAP.0b013e318295df80. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
