The Endocrine Function of Testes in 12- and 18-Month-Old Boars of Different Breeds
- PMID: 34824757
- PMCID: PMC8605855
- DOI: 10.22092/ari.2021.355354.1676
The Endocrine Function of Testes in 12- and 18-Month-Old Boars of Different Breeds
Abstract
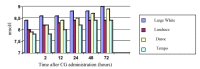
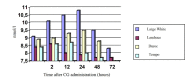
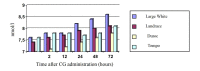
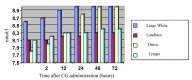
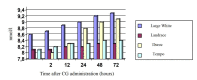
Testes have several primary functions, such as male gametes production (spermatozoa) and secretion of several endocrine factors, including the production of steroid and protein hormones which facilitate elements in the healthy reproductive function of mammals. The potential of an animal functional endocrine reservoir could be an interesting finding in animal reproduction management. Therefore, the current study aimed to analyze the functional endocrine reserves of testes in 12- and 18-month-old boars of four different boar breeds, namely Large White, Landrace, Duroc, and Tempo, as the animal model in this research (n=10). To determine the functional endocrine reserves of the testes at 12 and 18 months of age, boars received injections of human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) 3 times every 72 hours. Testosterone was measured in blood samples (10 mL) taken from the jugular vein before the administration of hCG as well as 2, 12, 24, 48, and 72 hours after administration of each of three hCG injections. The index of endocrine activity of the testes was determined by the formula: Ita = T1 -T0 / T0 , where Ita is the index of endocrine activity of the testes, T0 is the testosterone concentration before the administration of hCG, and T1 is the maximum testosterone concentration after the third administration of hCG. The effects of the hCG injection on boar testes at different age periods indicated that the testes of Large White and Duroc boars have higher potential endocrine reserves compared with the Landrace and Tempo breeds.
Keywords: Large White; chorionic gonadotropin; Duroc; Landrace; Tempo; boars; breeds; testosterone.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Differences in testosterone, androstenone, and skatole levels in plasma and fat between pubertal purebred Duroc and Landrace boars in response to human chorionic gonadotrophin stimulation.Theriogenology. 2010 Oct 1;74(6):1088-98. doi: 10.1016/j.theriogenology.2010.05.006. Epub 2010 Jun 26. Theriogenology. 2010. PMID: 20580070 Clinical Trial.
-
Semen characteristics, testicular size, and reproductive hormone concentrations in mature duroc, meishan, fengjing, and minzhu boars.Biol Reprod. 1993 Sep;49(3):515-21. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod49.3.515. Biol Reprod. 1993. PMID: 8399844
-
[Effect of chorionic gonadotropin administration on the concentration of testosterone in the blood of boars].Vet Med (Praha). 1979 Jun;24(6):321-9. Vet Med (Praha). 1979. PMID: 111397 Czech.
-
RFamide-related peptide 3 and gonadotropin-releasing hormone-II are autocrine-paracrine regulators of testicular function in the boar.Mol Reprod Dev. 2017 Sep;84(9):994-1003. doi: 10.1002/mrd.22830. Epub 2017 Jun 21. Mol Reprod Dev. 2017. PMID: 28475264 Review.
-
Genetic variation in sperm production.Soc Reprod Fertil Suppl. 2006;62:99-112. Soc Reprod Fertil Suppl. 2006. PMID: 16866312 Review.
References
-
- Pawlicki P, Duliban M, Tuz R, Ptak A, Milon A, Gorowska-Wojtowicz E, et al. Do G-protein coupled estrogen receptor and bisphenol A analogs influence on Leydig cell epigenetic regulation in immature boar testis ex vivo? . Anim Reprod Sci. 2019;207:21–35. - PubMed
-
- Tang W, Wu J, Jin S, He L, Lin Q, Luo F, et al. Glutamate and aspartate alleviate testicular/epididymal oxidative stress by supporting antioxidant enzymes and immune defense systems in boars. Sci China Life Sci. 2020;63(1):116–24. - PubMed
-
- Bielas W, Nizanski W, Nicpon J, Nicpon JE, Partyka A, Mordak R, et al. Effect of zearalenone on circulating testosterone concentration, testicular and epididymal morphology and epididymal sperm characteristics in wild boars. Theriogenology. 2017;102:59–66. - PubMed
-
- Kotula-Balak M, Duliban M, Pawlicki P, Tuz R, Bilinska B, Plachno BJ, et al. The meaning of non-classical estrogen receptors and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor for boar Leydig cell of immature testis. Acta Histochem. 2020;122(3):151526. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
