Proteostasis regulated by testis-specific ribosomal protein RPL39L maintains mouse spermatogenesis
- PMID: 34825148
- PMCID: PMC8605100
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2021.103396
Proteostasis regulated by testis-specific ribosomal protein RPL39L maintains mouse spermatogenesis
Abstract
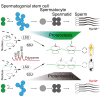
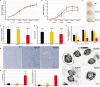
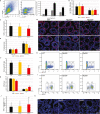
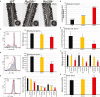
Maintaining proteostasis is important for animal development. How proteostasis influences spermatogenesis that generates male gametes, spermatozoa, is not clear. We show that testis-specific paralog of ribosomal large subunit protein RPL39, RPL39L, is required for mouse spermatogenesis. Deletion of Rpl39l in mouse caused reduced proliferation of spermatogonial stem cells, malformed sperm mitochondria and flagella, leading to sub-fertility in males. Biochemical analyses revealed that lack of RPL39L deteriorated protein synthesis and protein quality control in spermatogenic cells, partly due to reduced biogenesis of ribosomal subunits and ribosome homeostasis. RPL39/RPL39L is likely assembled into ribosomes via H/ACA domain containing NOP10 complex early in ribosome biogenesis pathway. Furthermore, Rpl39l null mice exhibited compromised regenerative spermatogenesis after chemical insult and early degenerative spermatogenesis in aging mice. These data demonstrate that maintaining proteostasis is important for spermatogenesis, of which ribosome homeostasis maintained by ribosomal proteins coordinates translation machinery to the regulation of cellular growth.
Keywords: Developmental biology; Male reproductive endocrinology; Molecular biology.
© 2021 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
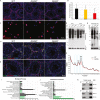


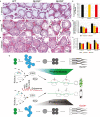
References
-
- Badertscher L., Wild T., Montellese C., Alexander L.T., Bammert L., Sarazova M., Stebler M., Csucs G., Mayer T.U., Zamboni N., et al. Genome-wide RNAi screening identifies protein modules required for 40s subunit synthesis in human cells. Cell. Rep. 2015;13:2879–2891. - PubMed
-
- Balch W.E., Morimoto R.I., Dillin A., Kelly J.W. Adapting proteostasis for disease intervention. Science. 2008;319:916–919. - PubMed
-
- Balchin D., Hayer-Hartl M., Hartl F.U. In vivo aspects of protein folding and quality control. Science. 2016;353:aac4354. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

