Optimization of extraction conditions and determination of the Chlorpyrifos, Diazinon, and malathion residues in environment samples: Fruit (Apple, Orange, and Tomato)
- PMID: 34825172
- PMCID: PMC8604744
- DOI: 10.1016/j.fochx.2021.100163
Optimization of extraction conditions and determination of the Chlorpyrifos, Diazinon, and malathion residues in environment samples: Fruit (Apple, Orange, and Tomato)
Abstract
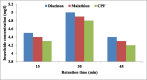
Organophosphate (OP) insecticide, such as diazinon is found in the environments like water which is still approved for agricultural uses. When diazinon residues enter the human body, it functions as an acetylcholinesterase (AChE) inhibitor. This research aims to measure of chlorpyrifos (CPF), diazinon, and malathion residues in fruit such as apple, orange, and tomato after optimizing extraction conditions. Pesticide residues are measured by gas chromatography (GC) technique. Effective variables on pesticide residues are studied including pesticides kind, sampling station, and fruit kind. Results show that average concentration CPF, diazinon, and malathion residues in orange water are 7.05 ± 0.01 mg L-1, 6.66 ± 0.03 mg L-1, and 12.38 ± 0.02 µgL-1, respectively. The average concentration CPF, diazinon, and malathion residues in apple water are 0.74 ± 0.02 mgL-1, 0.70 ± 0.01 mgL-1, and 1.10 ± 0.01 µgL-1, respectively. The average concentration CPF, diazinon, and malathion residues in tomato water are 0.60 ± 0.02 mgL-1, 0.57 ± 0.02 mgL-1, and 0.89 ± 0.01 µgL-1, respectively. The highest CPF concentration is observed in the orange fruit from station 20. Due to an appropriate storage condition and presenting organic fruits in the supermarket, the least mean concentration of pesticides is obtained in studied fruits from station 2. The manner of washing, peeling, and storage period before consuming fruits lead to decreasing studied pesticides concentration about 15-35, 40-50, and 50-60%, respectively. Increasing the fruit shelf-life led to decreasing studied pesticides concentration. Between pesticide concentration and variables: pesticides kind, sampling station, fruit kind, are not seen meaningful statistic relationship (P > 0.05). This study showed that pesticide residues in fruits can be decreased by washing, refrigerating, peeling procedures and increase in public surveillance.
Keywords: Chlorpyrifos (CPF); Diazinon; Environment sample; Gas chromatography (GC); Malathion; Organophosphate (OP).
© 2021 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Pesticides residues determination and probabilistic health risk assessment in the soil and cantaloupe by Monte Carlo simulation: A case study in Kashan and Aran-Bidgol, Iran.Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2023 Sep 15;263:115229. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2023.115229. Epub 2023 Jul 11. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2023. PMID: 37441953
-
Simultaneous determination of organophosphorus pesticides residues in vegetable, fruit juice, and milk samples with magnetic dispersive micro solid-phase extraction and chromatographic method; recruitment of simplex lattice mixture design for optimization of novel sorbent composites.Anal Chim Acta. 2021 Sep 15;1178:338802. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2021.338802. Epub 2021 Jun 28. Anal Chim Acta. 2021. PMID: 34482881
-
Alterations in reproductive hormone levels among farm women and their children occupationally exposed to organophosphate pesticides.Women Health. 2022 May-Jun;62(5):454-464. doi: 10.1080/03630242.2022.2085844. Epub 2022 Jun 8. Women Health. 2022. PMID: 35676759
-
A global systematic review, meta-analysis and health risk assessment on the quantity of Malathion, Diazinon and Chlorpyrifos in Vegetables.Chemosphere. 2021 May;270:129382. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.129382. Epub 2020 Dec 26. Chemosphere. 2021. PMID: 33418228
-
Some Organophosphate Insecticides and Herbicides.Lyon (FR): International Agency for Research on Cancer; 2017. Lyon (FR): International Agency for Research on Cancer; 2017. PMID: 31829533 Free Books & Documents. Review.
References
-
- Amirahmadi M., Yazdanpanah H., Shoeibi S., Pirali-Hamedani M., Gholami M.O., Mohseninia M.F., Kobarfard F. Simultaneous determination of 17 pesticide residues in rice by GC/MS using a direct sample introduction procedure and spiked calibration curves. Iranian Journal of Pharmaceutical Research: IJPR. 2013;12(2):295–302. doi: 10.22037/IJPR.2013.1303. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Baharum N.A., Nasir H.M., Ishak M.Y., Isa N.M., Hassan M.A., Aris A.Z. Highly efficient removal of diazinon pesticide from aqueous solutions by using coconut shell-modified biochar. Arabian Journal of Chemistry. 2020;13(7):6106–6121. doi: 10.1016/j.arabjc.2020.05.011. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

