The Historical Burden of Sporotrichosis in Brazil: a Systematic Review of Cases Reported from 1907 to 2020
- PMID: 34825345
- PMCID: PMC8882507
- DOI: 10.1007/s42770-021-00658-1
The Historical Burden of Sporotrichosis in Brazil: a Systematic Review of Cases Reported from 1907 to 2020
Abstract
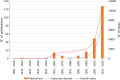
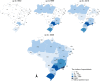
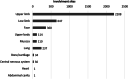
Sporotrichosis is a cosmopolitan subcutaneous mycosis caused by Sporothrix species. Recently, this mycosis has gained notoriety due to the appearance of new endemic areas, recognition of new pathogenic species, changes in epidemiology, occurrence of outbreaks, and increasing numbers of cases. The purpose of this study is to analyze the peculiarities of sporotrichosis cases in Brazil since its first report in the country until 2020. In this work, ecological, epidemiological, clinical, and laboratorial characteristics were compiled. A systematic review of human sporotrichosis diagnosed in Brazil and published up to December 2020 was performed on PubMed/MEDLINE, SciELO, Web of Science, and LILACS databases. Furthermore, animal sporotrichosis and environmental isolation of Sporothrix spp. in Brazil were also evaluated. The study included 230 papers, resulting in 10,400 human patients. Their ages ranged from 5 months to 92 years old and 55.98% were female. The lymphocutaneous form was predominant (56.14%), but systemic involvement was also notably reported (14.34%), especially in the lungs. Besides, hypersensitivity manifestations (4.55%) were described. Most patients had the diagnosis confirmed by isolation of Sporothrix spp., mainly from skin samples. Sporothrix brasiliensis was the major agent identified. HIV infection, cardiovascular diseases, and diabetes were the most common comorbidities. Cure rate was 85.83%. Concerning animal sporotrichosis, 8538 cases were reported, mostly in cats (90.77%). Moreover, 13 Sporothrix spp. environmental strains were reported. This review highlights the burden of the emergent zoonotic sporotrichosis in Brazil, reinforcing the importance of "One Health" based actions to help controlling this disease.
Keywords: Brazil; Clinical manifestation; Diagnosis; Sporothrix; Sporotrichosis.
© 2021. Sociedade Brasileira de Microbiologia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Chakrabarti A, Bonifaz A, Gutierrez-Galhardo MC, Mochizuki T, Li S. Global epidemiology of sporotrichosis. Med Mycol. 2015;53:3–14. - PubMed
-
- Rodrigues AM, Cruz Choappa R, Fernandes GF, de Hoog GS, de Camargo ZP. Sporothrix chilensis sp. nov. (Ascomycota: Ophiostomatales), a soil-borne agent of human sporotrichosis with mild-pathogenic potential to mammals. Fungal Biol. 2016;120:246–264. - PubMed
-
- Rodrigues AM, Terra Della PP, Gremião ID, Pereira SA, Orofino-Costa R, de Camargo ZP. The threat of emerging and re-emerging pathogenic Sporothrix species. Mycopathologia. 2020;185:813–842. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

