A review of center of pressure (COP) variables to quantify standing balance in elderly people: Algorithms and open-access code
- PMID: 34826208
- PMCID: PMC8623280
- DOI: 10.14814/phy2.15067
A review of center of pressure (COP) variables to quantify standing balance in elderly people: Algorithms and open-access code
Abstract
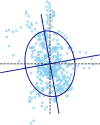
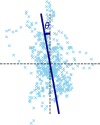
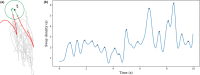
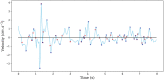
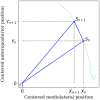
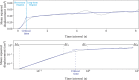
Postural control is often quantified by recording the trajectory of the center of pressure (COP)-also called stabilogram-during human quiet standing. This quantification has many important applications, such as the early detection of balance degradation to prevent falls, a crucial task whose relevance increases with the aging of the population. Due to the complexity of the quantification process, the analyses of sway patterns have been performed empirically using a number of variables, such as ellipse confidence area or mean velocity. This study reviews and compares a wide range of state-of-the-art variables that are used to assess the risk of fall in elderly from a stabilogram. When appropriate, we discuss the hypothesis and mathematical assumptions that underlie these variables, and we propose a reproducible method to compute each of them. Additionally, we provide a statistical description of their behavior on two datasets recorded in two elderly populations and with different protocols, to hint at typical values of these variables. First, the balance of 133 elderly individuals, including 32 fallers, was measured on a relatively inexpensive, portable force platform (Wii Balance Board, Nintendo) with a 25-s open-eyes protocol. Second, the recordings of 76 elderly individuals, from an open access database commonly used to test static balance analyses, were used to compute the values of the variables on 60-s eyes-open recordings with a research laboratory standard force platform.
Keywords: center of pressure; elderly; postural control; quiet standing.
© 2021 The Authors. Physiological Reports published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of The Physiological Society and the American Physiological Society.
Figures
References
-
- Alizadehsaravi, L. , Bruijn, S. M. , Maas, H. , & van Dieën, J. H. (2020). Modulation of soleus muscle H‐reflexes and ankle muscle co‐contraction with surface compliance during unipedal balancing in young and older adults. Experimental Brain Research, 238(6), 1371–1383., ISSN 0014‐4819, 1432‐1106. 10.1007/s00221-020-05784-0 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

