Treatment of UTIs Due to Klebsiella pneumoniae Carbapenemase-Producers: How to Use New Antibiotic Drugs? A Narrative Review
- PMID: 34827272
- PMCID: PMC8615227
- DOI: 10.3390/antibiotics10111332
Treatment of UTIs Due to Klebsiella pneumoniae Carbapenemase-Producers: How to Use New Antibiotic Drugs? A Narrative Review
Abstract
Background: K. pneumoniae is one of the bacteria most frequently causing health care-associated urinary tract infections, and increasingly incriminating Klebsiella pneumoniae carbapenemase producers (KPCp). Most infections caused by KPCp are nosocomial and might cause serious issues, even leading to death in half of the reported cases. Our aim was to identify the best strategy, based on available scientific data, for the use of new antibiotic treatments to manage KPCp UTIs.
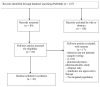
Methods: this narrative review of the literature was performed according to the criteria of preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analyses statement (PRISMA) (2020).
Results and conclusions: KPCp-UTIs are a real challenge for physicians. While cefiderocol, meropenem-vaborbactam, ceftazidim-avibactam, and imipenem-relebactam represent a major step forward in the treatment of these UTIs, no guidelines are currently available, in view of choosing the most appropriate treatment, in each specific case.
Keywords: KPC; PK/PD; UTI; antibiotic treatment; cefiderocol; ceftazidim-avibactam; imipenem-relebactam; meropenem-vaborbactam.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
-
- Cassini A., Högberg L.D., Plachouras D., Quattrocchi A., Hoxha A., Simonsen G.S., Colomb-Cotinat M., Kretzschmar M.E., Devleesschauwer B., Cecchini M., et al. Attributable deaths and disability-adjusted life-years caused by infections with antibiotic-resistant bacteria in the EU and the European Economic Area in 2015: A population-level modelling analysis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2019;19:56–66. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(18)30605-4. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Tacconelli E., Carrara E., Savoldi A., Harbarth S., Mendelson M., Monnet D.L., Pulcini C., Kahlmeter G., Kluytmans J., Carmeli Y., et al. Discovery, research, and development of new antibiotics: The WHO priority list of antibiotic-resistant bacteria and tuberculosis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2018;18:318–327. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(17)30753-3. - DOI - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization, editor. Antimicrobial Resistance: Global Report on Surveillance. World Health Organization; Geneva, Switzerland: 2014. p. 232.
-
- Zilberberg M.D., Shorr A.F. Secular Trends in Gram-Negative Resistance among Urinary Tract Infection Hospitalizations in the United States, 2000–2009. [(accessed on 21 April 2021)];Infect. Control. Hosp. Epidemiol. 2013 34:940–946. doi: 10.1086/671740. Available online: https://www.cambridge.org/core/journals/infection-control-and-hospital-e.... - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources