LncRNAs: Novel Biomarkers for Pancreatic Cancer
- PMID: 34827663
- PMCID: PMC8615627
- DOI: 10.3390/biom11111665
LncRNAs: Novel Biomarkers for Pancreatic Cancer
Abstract
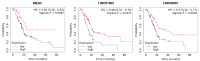
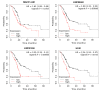
Pancreatic cancer is one of the most deadly neoplasms and the seventh major cause of cancer-related deaths among both males and females. This cancer has a poor prognosis due to the lack of appropriate methods for early detection of cancer. Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) have been recently found to influence the progression and initiation of pancreatic cancer. MACC1-AS1, LINC00976, LINC00462, LINC01559, HOXA-AS2, LINC00152, TP73-AS1, XIST, SNHG12, LUCAT1, and UCA1 are among the oncogenic lncRNAs in pancreatic cancer. On the other hand, LINC01111, LINC01963, DGCR5, MEG3, GAS5, and LINC00261 are among tumor suppressor lncRNAs in this tissue. In the current review, we summarize the roles of these two classes of lncRNAs in pancreatic cancer and discuss their potential as attractive diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers for pancreatic cancer. We also identified that the low expression of MEG3, LINC01963, and LINC00261 and the high expression of MACC1-AS1, LINC00462, LINC01559, and UCA1 were significantly correlated with worse survival in pancreatic cancer patients. Further research on these lncRNAs will provide new clues that could potentially improve the early diagnosis, prognostic prediction, and personalized treatments of patients with pancreatic cancer.
Keywords: biomarker; diagnosis; lncRNAs; pancreatic cancer; prognosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Siegel R.L., Miller K.D., Fuchs H.E., Jemal A. Cancer Statistics, 2021. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2021;71:7–33. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

