Using a Socio-Environmental Approach to Explore the Determinants for Meeting the Recommended Physical Activity among Adults at Risk of Diabetes in Rural Indonesia
- PMID: 34828514
- PMCID: PMC8618249
- DOI: 10.3390/healthcare9111467
Using a Socio-Environmental Approach to Explore the Determinants for Meeting the Recommended Physical Activity among Adults at Risk of Diabetes in Rural Indonesia
Abstract
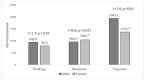
Moderate-to-vigorous physical activity (PA) is recommended to mitigate the risk of diabetes. This study explored the PA of adults at risk for diabetes in rural Indonesia and determined the requirements for meeting the recommended PA level. In total, 842 adults were screened using a diabetes risk test in a rural health centre; among them, 342 were at risk of diabetes. The level of PA was assessed using the International Physical Activity Questionnaire, whereas the associated factors underlying the three domains -individual, support, and environment-were determined by the Influences on Physical Activity Instrument. The data analysis included a three-step multiple linear regression (MLR) and logistic regression (LR). Overall, 40.6% of the participants met the recommended PA. According to the MLR analysis, among males, individuals who gave PA a higher priority and had enough time to perform PA were predicted to have a higher activity energy expenditure (MET-minutes per week). According to the LR analysis, men were more likely to meet the recommended PA, and people who gave PA a lower priority and had less access to space for PA were less likely to meet the recommended PA level. Strategies for promoting PA in rural Indonesia include focusing on women, people who prioritize PA less, and those who have less time and space in which to be physically active.
Keywords: culture; physical activity; prediabetic state; social environments.
Conflict of interest statement
We declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Physical Activity Patterns and Neighborhood Characteristics of First-Generation Latina Immigrants Living in Arizona: Cross-sectional Study.JMIR Form Res. 2021 May 17;5(5):e25663. doi: 10.2196/25663. JMIR Form Res. 2021. PMID: 33999003 Free PMC article.
-
Meeting Recommended Levels of Physical Activity and Health-Related Quality of Life in Rural Adults.J Lifestyle Med. 2016 Mar;6(1):1-6. doi: 10.15280/jlm.2016.6.1.1. Epub 2016 Mar 31. J Lifestyle Med. 2016. PMID: 27358834 Free PMC article.
-
Likelihood of meeting physical activity guidelines in rural and urban adults: cross-sectional analysis of the Canadian Community Health Survey.Can J Public Health. 2021 Aug;112(4):748-757. doi: 10.17269/s41997-021-00507-6. Epub 2021 May 12. Can J Public Health. 2021. PMID: 33977500 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence, patterns, and correlates of physical activity in Nepal: findings from a nationally representative study using the Global Physical Activity Questionnaire (GPAQ).BMC Public Health. 2019 Jul 3;19(1):864. doi: 10.1186/s12889-019-7215-1. BMC Public Health. 2019. PMID: 31269984 Free PMC article.
-
Meeting Recommended Levels of Physical Activity in Relation to Preventive Health Behavior and Health Status Among Adults.J Prev Med Public Health. 2017 Jan;50(1):10-17. doi: 10.3961/jpmph.16.080. J Prev Med Public Health. 2017. PMID: 28173688 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Saeedi P., Petersohn I., Salpea P., Malanda B., Karuranga S., Unwin N., Colagiuri S., Guariguata L., Motala A.A., Ogurtsova K., et al. Global and regional diabetes prevalence estimates for 2019 and projections for 2030 and 2045: Results from the International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas, 9th edition. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2019;157:107843. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2019.107843. - DOI - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization Physical Activity. 26 November 2020. [(accessed on 18 May 2021)]. Available online: http://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/physical-activity.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous