The Effect of Pulsed Electric Fields (PEF) Combined with Temperature and Natural Preservatives on the Quality and Microbiological Shelf-Life of Cantaloupe Juice
- PMID: 34828887
- PMCID: PMC8622698
- DOI: 10.3390/foods10112606
The Effect of Pulsed Electric Fields (PEF) Combined with Temperature and Natural Preservatives on the Quality and Microbiological Shelf-Life of Cantaloupe Juice
Abstract
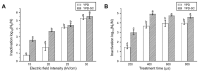
Pulsed electric field (PEF) is an innovative, non-thermal technology for food preservation with many superiorities. However, the sub-lethally injured microorganisms caused by PEF and their recovery provide serious food safety problems. Our study examined the effects of pH, temperature and natural preservatives (tea polyphenols and natamycin) on the recovery of PEF-induced, sub-lethally injured Saccharomyces cerevisiae cells, and further explored the bactericidal effects of the combined treatments of PEF with the pivotal factors in cantaloupe juice. We first found that low pH (pH 4.0), low temperature (4 °C), tea polyphenols and natamycin inhibited the recovery of injured S. cerevisiae cells. Then, the synergistic effects of PEF, combined with cold-temperature storage (4 °C), a mild treatment temperature (50 and 55 °C), tea polyphenols or natamycin, on the inactivation of S. cerevisiae in cantaloupe juice were evaluated. Our results showed that the combination of PEF and heat treatment, tea polyphenols or natamycin enhanced the inactivation of S. cerevisiae and reduced the level of sub-lethally injured cells. Moreover, PEF combined with 55 °C heat treatment or tea polyphenols was applied for cantaloupe juice. In the practical application, the two combined PEF methods displayed a comparable inactivation heat pasteurization ability, prolonged the shelf life of juice compared with PEF treatment alone, and better preserved the physicochemical properties and vitamin C levels of cantaloupe juice. These results provide valuable information to inhibit the recovery of PEF-injured microbial cells and shed light on the combination of PEF with other factors to inactivate microorganisms for better food preservation.
Keywords: Saccharomyces cerevisiae; cantaloupe juice; natural preservatives; physicochemical characteristics; pulsed electric fields; shelf life; temperature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Putnik P., Kresoja Ž., Bosiljkov T., Režek Jambrak A., Barba F.J., Lorenzo J.M., Roohinejad S., Granato D., Žuntar I., Bursać Kovačević D. Comparing the Effects of Thermal and Non-Thermal Technologies on Pomegranate Juice Quality: A Review. Food Chem. 2019;279:150–161. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.11.131. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Zhang Z.H., Wang L.H., Zeng X.A., Han Z., Brennan C.S. Non-Thermal Technologies and Its Current and Future Application in the Food Industry: A Review. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019;54:1–13. doi: 10.1111/ijfs.13903. - DOI
-
- Bhattacharjee C., Saxena V.K., Dutta S. Novel Thermal and Non-Thermal Processing of Watermelon Juice. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019;93:234–243. doi: 10.1016/j.tifs.2019.09.015. - DOI
-
- Arshad R.N., Abdul-Malek Z., Roobab U., Munir M.A., Naderipour A., Qureshi M.I., El-Din Bekhit A., Liu Z.-W., Aadil R.M. Pulsed Electric Field: A Potential Alternative towards a Sustainable Food Processing. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021;111:43–54. doi: 10.1016/j.tifs.2021.02.041. - DOI
-
- Jin T.Z., Zhang H. Food Safety Engineering. Springer; Cham, Switzerland: 2020. Pulsed Electric Fields for Pasteurization: Food Safety and Shelf Life; pp. 553–577.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

