Astragalus Polysaccharides and Saponins Alleviate Liver Injury and Regulate Gut Microbiota in Alcohol Liver Disease Mice
- PMID: 34828972
- PMCID: PMC8623381
- DOI: 10.3390/foods10112688
Astragalus Polysaccharides and Saponins Alleviate Liver Injury and Regulate Gut Microbiota in Alcohol Liver Disease Mice
Abstract
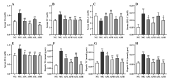
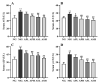
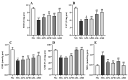
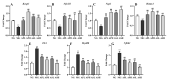
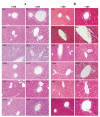
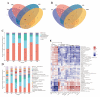
Astragalus, a medical and edible plant in China, shows several bioactive properties. However, the role of astragalus in attenuating alcoholic liver disease (ALD) is less clear. The objective of this project is to investigate the improving effect of astragalus saponins (AS) and astragalus polysaccharides (AP), which are the two primary constituents in astragalus on hepatic injury induced by alcohol, and the potential mechanisms of action. Different doses of AS (50 and 100 mg/kg bw) and AP (300 and 600 mg/kg bw) were orally given to alcohol-treated mice for four weeks. The results demonstrated that both AP and AS could reverse the increase of the levels of TC, TG, FFA, and LDL-C in serum, and the decrease of serum HDL-C content, as well as the elevation of hepatic TC and TG levels induced by alcohol. The activities of AST, ALT, ALP, and γ-GT in ALD mice were raised after AP and AS supplementation. The antioxidant markers (SOD, CAT, GSH, and GSH-Px) were obviously augmented and the pro-inflammatory cytokines (TNF-α, IL-6 and IL-1β) and hepatic histological variations were alleviated by AP and AS, which was in line with the levels of oxidative stress-associated genes (Keap1, Nfe2l2, Nqo1, and Hmox1) and inflammation-associated genes (Tlr4, Myd88 and Nfkb1). In addition, AS exerted a more efficient effect than AP and the results presented dose proportionality. Moreover, AS and AP could modulate the intestinal microbiota disturbance induced by alcohol. Overall, AS and AP administration could ameliorate lipid accumulation in the serum and liver, as well as hepatic function, oxidative stress, inflammatory response, and gut flora disorders in mice as a result of alcohol.
Keywords: alcoholic liver disease; astragalus; gut microbiota; polysaccharides; saponins.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

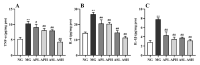
Similar articles
-
The hepatoprotective effects of Sedum sarmentosum extract and its isolated major constituent through Nrf2 activation and NF-κB inhibition.Phytomedicine. 2019 Feb;53:263-273. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2018.09.023. Epub 2018 Sep 3. Phytomedicine. 2019. PMID: 30668406
-
Antrodin A from mycelium of Antrodia camphorata alleviates acute alcoholic liver injury and modulates intestinal flora dysbiosis in mice.J Ethnopharmacol. 2020 May 23;254:112681. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.112681. Epub 2020 Feb 19. J Ethnopharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32087320
-
Protective Effects of Ellagic Acid Against Alcoholic Liver Disease in Mice.Front Nutr. 2021 Sep 14;8:744520. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2021.744520. eCollection 2021. Front Nutr. 2021. PMID: 34595202 Free PMC article.
-
Amelioration of CCl4-induced liver injury in rats by selenizing Astragalus polysaccharides: Role of proinflammatory cytokines, oxidative stress and hepatic stellate cells.Res Vet Sci. 2017 Oct;114:202-211. doi: 10.1016/j.rvsc.2017.05.002. Epub 2017 May 2. Res Vet Sci. 2017. PMID: 28482267
-
n-3 Polyunsaturated fatty acids for the management of alcoholic liver disease: A critical review.Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2019;59(sup1):S116-S129. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2018.1544542. Epub 2018 Dec 22. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2019. PMID: 30580553 Review.
Cited by
-
Qinggan Huoxue Recipe attenuates Alcoholic Liver Disease by suppressing PI3K/AKT signaling pathway based on network pharmacology.Int J Med Sci. 2023 Jan 31;20(3):346-358. doi: 10.7150/ijms.80329. eCollection 2023. Int J Med Sci. 2023. PMID: 36860681 Free PMC article.
-
The Antioxidant Action of Astragali radix: Its Active Components and Molecular Basis.Molecules. 2024 Apr 9;29(8):1691. doi: 10.3390/molecules29081691. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38675511 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The impact of traditional Chinese medicine and dietary compounds on modulating gut microbiota in hepatic fibrosis: A review.Heliyon. 2024 Sep 26;10(19):e38339. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e38339. eCollection 2024 Oct 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39391468 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hepatoprotective effects of peach gum polysaccharides against alcoholic liver injury: moderation of oxidative stress and promotion of lipid metabolism.Front Nutr. 2024 Jan 11;10:1325450. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2023.1325450. eCollection 2023. Front Nutr. 2024. PMID: 38283909 Free PMC article.
-
Gut microbiota: A magical multifunctional target regulated by medicine food homology species.J Adv Res. 2023 Oct;52:151-170. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2023.05.011. Epub 2023 Jun 2. J Adv Res. 2023. PMID: 37269937 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Allam R.M., Selim D.A., Ghoneim A.I., Radwan M.M., Nofal S.M., Khalifa A.E., Sharaf O.A., Toaima S.M., Asaad A.M., El-Sebakhy N.A. Hepatoprotective effects of Astragalus kahiricus root extract against ethanol-induced liver apoptosis in rats. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2013;11:354–361. doi: 10.1016/S1875-5364(13)60052-7. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

