The Prevalence and Epidemiology of Salmonella in Retail Raw Poultry Meat in China: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 34829037
- PMCID: PMC8622452
- DOI: 10.3390/foods10112757
The Prevalence and Epidemiology of Salmonella in Retail Raw Poultry Meat in China: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
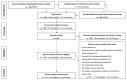
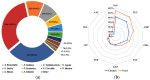
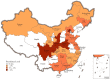
Foodborne disease caused by Salmonella is an important public health concern worldwide. Animal-based food, especially poultry meat, is the main source of human salmonellosis. The objective of this study was to evaluate the prevalence and epidemiology of Salmonella contamination in raw poultry meat commercialized in China. Following the principle of systematic review, 98 sets of prevalence data were extracted from 74 publications conducted in 21 Chinese provincial regions. The random-effect model was constructed for subgrouping analysis by meat category, preservation type, and geographical location. The prevalence levels differed from high to low among raw poultry meat, including chicken, 26.4% (95% CI: 22.4-30.8%); pigeon, 22.6% (95% CI: 18.2-27.8%); duck, 10.1% (95% CI: 5.3-18.2%); and other poultry meat, 15.4% (95% CI: 12.0-19.5%). Prevalence data on the preservation type revealed that chilled poultry meat might be more likely to experience cross-contamination than non-chilled poultry meat in China. The distribution map of Salmonella for raw poultry meat showed that a higher prevalence level was found in the Shaanxi, Henan, Sichuan, and Beijing regions. All subgroups possessed high amounts of heterogeneity (I2 > 75%). The scientific data regarding the differences in prevalence levels between meat category, preservation method, and geographical region sources might be useful to improve specific interventions to effectively control the incidence of Salmonella in poultry meat.
Keywords: antibiotic resistance; chicken; food safety; foodborne pathogen; microbial contamination; salmonellosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Zhu J.H., Wang Y.R., Song X.Y., Cui S.H., Xu H.B., Yang B.W., Huang J.L., Liu G.H., Chen Q., Zhou G., et al. Prevalence and quantification of Salmonella contamination in raw chicken carcasses at the retail in China. Food Cont. 2014;44:198–202. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2014.03.050. - DOI
-
- Cai Y.Q., Tao J., Jiao Y., Fei X., Zhou L., Wang Y., Zheng H.J., Pan Z.M., Jiao X.N. Phenotypic characteristics and genotypic correlation between Salmonella isolates from a slaughterhouse and retail markets in Yangzhou, China. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2016;222:56–64. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2016.01.020. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

