High-Resolution Computed Tomography: Lights and Shadows in Improving Care for SSc-ILD Patients
- PMID: 34829307
- PMCID: PMC8617987
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics11111960
High-Resolution Computed Tomography: Lights and Shadows in Improving Care for SSc-ILD Patients
Abstract
The diagnosis and classification of systemic sclerosis-associated interstitial lung disease (SSc-ILD) is essential to improve the prognosis of systemic sclerosis (SSc) patients. The risk-stratification of disease severity and follow-up requires a multidisciplinary approach, integrating high-resolution computed tomography (HRTC) of the lung, pulmonary function tests (PFT), along with clinical and symptomatic evaluations. The use of HRCT in detecting SSc-ILD is not so much based on a definitive validation, but rather reflects the widespread clinician recognition of dissatisfaction with other modalities. However, due to the heterogeneity of SSc-ILD and the potential absence of symptoms in early or mild disease, it is prudent to consider as many parameters as possible in the assessment and monitoring of newly diagnosed patients. An early diagnosis meets the primary goal, i.e., the prevention of disease progression. The current first line treatment regimens are mainly centered on immunosuppressive therapy. This review assesses the role HRCT plays in optimizing care and improving clinical outcomes in SSc-ILD patients.
Keywords: high-resolution computed tomography (HRTC); interstitial lung disease (ILD); pulmonary function tests (PFT); systemic sclerosis (SSc); systemic sclerosis-associated interstitial lung disease (SSc-ILD); usual interstitial pneumonia (UIP).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



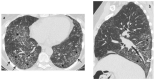

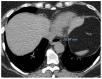
References
-
- Clukers J., Lukers J., Lanclus M., Belmans D., van Holsbeke C., de Backer W., Vummidi D., Cronin P., Lavon B.R., de Backer J., et al. Interstitial lung disease in systemic sclerosis quantification of disease classification and progression with high-resolution computed tomography: An observational study. J. Scleroderma Relat. Disord. 2021;6:154–164. doi: 10.1177/2397198320985377. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Tyndall A.J., Bannert B., Vonk M., Airò P., Cozzi F., Carreira P.E., Bancel D.F., Allanore Y., Müller-Ladner U., Distler O., et al. Causes and risk factors for death in systemic sclerosis: A study from the EULAR Scleroderma Trials and Research (EUSTAR) database. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2010;69:1809–1815. doi: 10.1136/ard.2009.114264. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

