Role of Endoscopic Ultrasound in Liver Disease: Where Do We Stand?
- PMID: 34829368
- PMCID: PMC8618190
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics11112021
Role of Endoscopic Ultrasound in Liver Disease: Where Do We Stand?
Abstract
As the burden of liver disease in the general populace steadily increases, so does the need for both advanced diagnostic and treatment options. Endoscopic ultrasound is a reliable diagnostic and therapeutic method that has an established role, foremost in pancreatobiliary pathology. This paper aims to summarize the growing role of endoscopic ultrasound in hepatology based on the search of the current literature. A number of applications of endoscopic ultrasound are reviewed, including both noninvasive methods and tissue acquisition in focal and diffuse liver disease, portal hypertension measurement, detection and management of gastric and esophageal varices, treatment of focal liver lesions and staging of pancreatobiliary malignancies, treatment of cystic and solid liver lesions, as well as liver abscess drainage. Both hepatologists and endoscopists should be aware of the evolving role of endoscopic ultrasound in liver disease. The inherent invasive nature of endoscopic examination limits its use to a targeted population identified using noninvasive methods. Endoscopic ultrasound is one the most versatile methods in gastroenterology, allowing immediate access with detection, sampling, and treatment of digestive tract pathology. Further expansion of its use in hepatology is immanent.
Keywords: EUS; chronic liver disease; endoscopic ultrasound; hepatology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest regarding this manuscript.
Figures

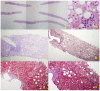
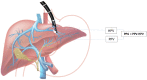
References
-
- GBD 2017 Disease and Injury Incidence and Prevalence Collaborators Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 354 diseases and injuries for 195 countries and territories, 1990-2017: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet. 2019;392:1789–1858. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736-18-32279-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Eddowes P., Sasso M., Allison M., Tsochatzis E., Anstee Q.M., Sheridan D., Guha I.N., Cobbold J.F., Deeks J.J., Paradis V., et al. Accuracy of FibroScan Controlled Attenuation Parameter and Liver Stiffness Measurement in Assessing Steatosis and Fibrosis in Patients with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Gastroenterology. 2019;156:1717–1730. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2019.01.042. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

