Neuroprotective Activity of Melittin-The Main Component of Bee Venom-Against Oxidative Stress Induced by Aβ25-35 in In Vitro and In Vivo Models
- PMID: 34829525
- PMCID: PMC8614890
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox10111654
Neuroprotective Activity of Melittin-The Main Component of Bee Venom-Against Oxidative Stress Induced by Aβ25-35 in In Vitro and In Vivo Models
Abstract
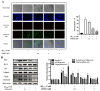
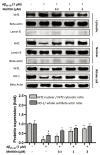
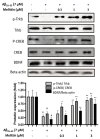
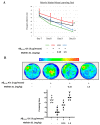
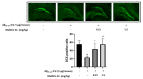
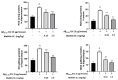
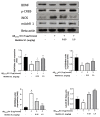
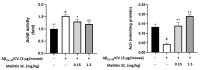
Melittin, a 26-amino acid peptide, is the main component of the venom of four honeybee species and exhibits neuroprotective actions. However, it is unclear how melittin ameliorates neuronal cells in oxidative stress and how it affects memory impairment in an in vivo model. We evaluated the neuroprotective effect of melittin on Aβ25-35-induced neuro-oxidative stress in both in vitro HT22 cells and in vivo animal model. Melittin effectively protected against HT22 cell viability and significantly deregulated the Aβ25-35-induced overproduction of intracellular reactive oxygen species. Western blot analysis showed that melittin suppressed cell apoptosis and regulated Bax/Bcl-2 ratio, as well as the expression of proapoptotic related factors: Apoptosis-inducing factor (AIF), Calpain, Cytochrome c (CytoC), Cleaved caspase-3 (Cleacas3). Additionally, melittin enhanced the antioxidant defense pathway by regulating the nuclear translocation of nuclear factor erythroid 2-like 2 (Nrf2) thus upregulated the production of the heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1), a major cellular antioxidant enzyme combating neuronal oxidative stress. Furthermore, melittin treatment activated the Tropomyosin-related kinase receptor B (TrkB)/cAMP Response Element-Binding (CREB)/Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), contributing to neuronal neurogenesis, and regulating the normal function of synapses in the brain. In our in vivo experiment, melittin was shown to enhance the depleted learning and memory ability, a novel finding. A mouse model with cognitive deficits induced by Aβ25-35 intracerebroventricular injection was used. Melittin had dose-dependently enhanced neural-disrupted animal behavior and enhanced neurogenesis in the dentate gyrus hippocampal region. Further analysis of mouse brain tissue and serum confirmed that melittin enhanced oxidant-antioxidant balance, cholinergic system activity, and intercellular neurotrophic factors regulation, which were all negatively altered by Aβ25-35. Our study shows that melittin exerts antioxidant and neuroprotective actions against neural oxidative stress. Melittin can be a potential therapeutic agent for neurodegenerative disorders.
Keywords: BDNF; bee venom; beta amyloid; melittin; neurodegeneration; oxidative stress.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Bee Venom Activates the Nrf2/HO-1 and TrkB/CREB/BDNF Pathways in Neuronal Cell Responses against Oxidative Stress Induced by Aβ1-42.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jan 21;23(3):1193. doi: 10.3390/ijms23031193. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35163115 Free PMC article.
-
Melittin - the main component of bee venom: a promising therapeutic agent for neuroprotection through keap1/Nrf2/HO-1 pathway activation.Chin Med. 2024 Nov 28;19(1):166. doi: 10.1186/s13020-024-01020-x. Chin Med. 2024. PMID: 39605070 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroprotective action of N-acetyl serotonin in oxidative stress-induced apoptosis through the activation of both TrkB/CREB/BDNF pathway and Akt/Nrf2/Antioxidant enzyme in neuronal cells.Redox Biol. 2017 Apr;11:592-599. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2016.12.034. Epub 2017 Jan 6. Redox Biol. 2017. PMID: 28110215 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroprotection Against Oxidative Stress: Phytochemicals Targeting TrkB Signaling and the Nrf2-ARE Antioxidant System.Front Mol Neurosci. 2020 Jul 2;13:116. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2020.00116. eCollection 2020. Front Mol Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32714148 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bee Venom Components as Therapeutic Tools against Prostate Cancer.Toxins (Basel). 2021 May 7;13(5):337. doi: 10.3390/toxins13050337. Toxins (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34067049 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Bee-Inspired Healing: Apitherapy in Veterinary Medicine for Maintenance and Improvement Animal Health and Well-Being.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Aug 9;17(8):1050. doi: 10.3390/ph17081050. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39204155 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic Use of Bee Venom and Potential Applications in Veterinary Medicine.Vet Sci. 2023 Feb 4;10(2):119. doi: 10.3390/vetsci10020119. Vet Sci. 2023. PMID: 36851423 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transferrin-Conjugated Melittin-Loaded L-Arginine-Coated Iron Oxide Nanoparticles for Mitigating Beta-Amyloid Pathology of the 5XFAD Mouse Brain.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Oct 6;24(19):14954. doi: 10.3390/ijms241914954. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37834402 Free PMC article.
-
Elimination of certain honeybee venom activities by adipokinetic hormone.Sci Rep. 2025 May 28;15(1):18638. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-02285-4. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40436933 Free PMC article.
-
Beneficial Effect of Bee Venom and Its Major Components on Facial Nerve Injury Induced in Mice.Biomolecules. 2023 Apr 17;13(4):680. doi: 10.3390/biom13040680. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 37189427 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

