The Protective Effect of Taurine on Oxidized Fish-Oil-Induced Liver Oxidative Stress and Intestinal Barrier-Function Impairment in Juvenile Ictalurus punctatus
- PMID: 34829560
- PMCID: PMC8615020
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox10111690
The Protective Effect of Taurine on Oxidized Fish-Oil-Induced Liver Oxidative Stress and Intestinal Barrier-Function Impairment in Juvenile Ictalurus punctatus
Abstract
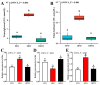
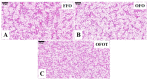
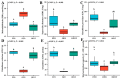
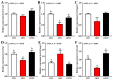
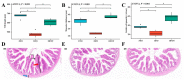
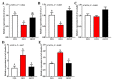
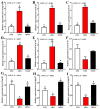
Dietary lipids provide energy for growth and development and provide fatty acids necessary for normal structure and biological function. However, oxidized lipids cause oxidative stress and intestinal damage. An 8-week feeding trial with fresh fish oil (FFO, control group), oxidized fish oil (OFO), and taurine-supplemented diets (OFOT, OFO + 0.2% of taurine) was conducted to evaluate the protective effect of taurine on oxidized fish-oil-induced liver oxidative stress and intestine impairment in juvenile Ictaluruspunctatus. The results showed that (1) Growth performance was significantly lower in fish fed OFO than in those fed other diets, whereas the opposite occurred in the hepatosomatic index. (2) OFO-feeding significantly increased lipid deposition compared with the FFO group. The addition of taurine ameliorated the OFO-induced increase in lipid vacuolization in the liver, significantly upregulated lpl mRNA expression, and downregulated fas and srebp1 mRNA expression. (3) OFO-feeding significantly reduced oxidative damage of liver. Compared with the OFO group, the OFOT group remarkably upregulated antioxidant enzyme mRNA expression through the Nrf2-Keap1 signaling pathway based on the transcriptional expression. (4) OFO diets induced intestinal physical and immune barrier damage. Compared with the OFO group, OFOT diets remarkably downregulated il-1β, il-6, tnf-α, and il-8 mRNA expression and upregulated tgf-β mRNA expression through the NF-κB signaling pathway. Besides, the addition of taurine to OFO diets significantly upregulated zo-2 and zo-1 mRNA expression, and downregulated claudin-15 and claudin-12 mRNA expression. In conclusion, oxidized-fish-oil diets can cause negative physiological health effects in Ictaluruspunctatus, while adding taurine can increase growth and antioxidant ability, reduce lipid deposition, and improve intestinal health.
Keywords: channel catfish; immune response; intestinal health; oxidative damage; signaling pathway.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. Although Dr. Jiancheng Zhou is from the Wuhan Dabeinong Aquatic Science and Technology Co. Ltd., the company had no role in the design of the study in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Taurine Attenuates Oxidized Fish Oil-Induced Oxidative Stress and Lipid Metabolism Disorder in Mice.Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Jul 18;11(7):1391. doi: 10.3390/antiox11071391. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35883883 Free PMC article.
-
Protective effects of chlorogenic acid on growth, intestinal inflammation, hepatic antioxidant capacity, muscle development and skin color in channel catfish Ictalurus punctatus fed an oxidized fish oil diet.Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2023 Mar;134:108511. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2022.108511. Epub 2023 Jan 1. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36599381
-
Changes in growth performance, haematological parameters, hepatopancreas histopathology and antioxidant status of pacific white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) fed oxidized fish oil: Regulation by dietary myo-inositol.Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019 May;88:53-64. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2019.02.023. Epub 2019 Feb 18. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30790659
-
Effects of Apple Polyphenols and Taurine on Growth Performance, Tissue Morphology, and Lipid and Glucose Metabolism in Rice Field Eel (Monopterus albus) Fed High Oxidized Fish Oil.Aquac Nutr. 2023 Nov 29;2023:4912141. doi: 10.1155/2023/4912141. eCollection 2023. Aquac Nutr. 2023. PMID: 38077279 Free PMC article.
-
Supplemental Xylooligosaccharide Modulates Intestinal Mucosal Barrier and Cecal Microbiota in Laying Hens Fed Oxidized Fish Oil.Front Microbiol. 2021 Feb 22;12:635333. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.635333. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33692770 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Antioxidants in Animal Feed.Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Sep 6;11(9):1760. doi: 10.3390/antiox11091760. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36139834 Free PMC article.
-
Feed Restriction Alleviates Chronic Thermal Stress-Induced Liver Oxidation and Damages via Reducing Lipid Accumulation in Channel Catfish (Ictalurus punctatus).Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 May 17;11(5):980. doi: 10.3390/antiox11050980. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35624844 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of cysteine addition to low-fishmeal diets on the growth, anti-oxidative stress, intestine immunity, and Streptococcus agalactiae resistance in juvenile golden pompano (Trachinotus ovatus).Front Immunol. 2022 Nov 17;13:1066936. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1066936. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36466908 Free PMC article.
-
Protective effects of yeast extract against alcohol-induced liver injury in rats.Front Microbiol. 2023 Jul 20;14:1217449. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1217449. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37547679 Free PMC article.
-
Engineered Bacillus subtilis alleviates intestinal oxidative injury through Nrf2-Keap1 pathway in enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC) K88-infected piglet.J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2023 Jun 15;24(6):496-509. doi: 10.1631/jzus.B2200674. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2023. PMID: 37309041 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sargent J., Bell G., McEvoy L., Tocher D., Estevez A. Recent developments in the essential fatty acid nutrition of fish. Aquaculture. 1999;177:191–199. doi: 10.1016/S0044-8486(99)00083-6. - DOI
-
- Zhou L., Han D., Zhu X., Yang Y., Jin J., Xie S. Effects of total replacement of fish oil by pork lard or rapeseed oil and recovery by a fish oil finishing diet on growth, health and fish quality of gibel carp (Carassius auratus gibelio) Aquac. Res. 2016;47:2961–2975. doi: 10.1111/are.12748. - DOI
-
- Gray J.I. Measurement of lipid oxidation: A review. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 1978;55:539–546. doi: 10.1007/BF02668066. - DOI
-
- Chen Y.J., Liu Y.J., Yang H.J., Yuan Y., Liu F.J., Tian L.X., Liang G.Y., Yuan R.M. Effect of dietary oxidized fish oil on growth performance, body composition, antioxidant defence chanism and liver histology of juvenile largemouth bass Micropterus salmoides. Aquac. Nutr. 2012;18:321–331. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2095.2011.00900.x. - DOI
-
- Liu D., Chi S., Tan B., Dong X., Yang Q., Liu H., Zhang S., Han F., He Y. Effects of fish oil with difference oxidation degree on growth performance and expression abundance of antioxidant and fat metabolism genes in orange spotted grouper, Epinephelus coioides. Aquac. Res. 2019;50:188–197. doi: 10.1111/are.13883. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

