Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway in Experimental Model of Fibromyalgia: Role of Hidrox®
- PMID: 34829912
- PMCID: PMC8615925
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines9111683
Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway in Experimental Model of Fibromyalgia: Role of Hidrox®
Abstract
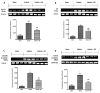
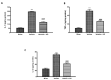
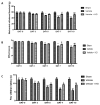
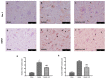
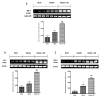
Fibromyalgia (FM) is a chronic condition characterized by persistent widespread pain that negatively affects the quality of life of patients. The WNT/β-catenin signaling pathway seems to be involved in central sensitization and different pain states. The objective of this study was to investigate the beneficial effects of a new compound called Hidrox® (HD), containing 40-50% hydroxytyrosol, in counteracting the pain associated with FM. An FM-like model was induced in rats by subcutaneous injections of reserpine (1 mg/kg) for three consecutive days. Later, HD (10 mg/kg) was administered orally to the animals for seven days. Reserpine injections induced WNT/β-catenin pathway activation, release of pro-inflammatory mediators as well as a significant increase in oxidative stress. Daily treatment with HD was able to modulate the WNT/β-catenin and Nrf2 pathways and consequently attenuate the behavioral deficits and microglia activation induced by reserpine injection. These results indicate that nutritional consumption of HD can be considered as a new therapeutic approach for human FM.
Keywords: Nrf2 pathway; WNT/β-catenin pathway; fibromyalgia; pain.
Conflict of interest statement
Roberto Crea is the president of Oliphenol LLC. and owns a patent for the Hidrox compound. The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- De la Luz-Cuellar Y.E., Rodriguez-Palma E.J., Franco-Enzastiga U., Salinas-Abarca A.B., Delgado-Lezama R., Granados-Soto V. Blockade of spinal alpha5-GABAA receptors differentially reduces reserpine-induced fibromyalgia-type pain in female rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2019;858:172443. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2019.172443. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Jensen K.B., Loitoile R., Kosek E., Petzke F., Carville S., Fransson P., Marcus H., Williams S.C., Choy E., Mainguy Y., et al. Patients with fibromyalgia display less functional connectivity in the brain’s pain inhibitory network. Mol. Pain. 2012;8:32. doi: 10.1186/1744-8069-8-32. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Fusco R., Siracusa R., D’Amico R., Peritore A.F., Cordaro M., Gugliandolo E., Crupi R., Impellizzeri D., Cuzzocrea S., Di Paola R. Melatonin Plus Folic Acid Treatment Ameliorates Reserpine-Induced Fibromyalgia: An Evaluation of Pain, Oxidative Stress, and Inflammation. Antioxidants. 2019;8:628. doi: 10.3390/antiox8120628. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

