Expression of Specific Alleles of Zinc-Finger Transcription Factors, HvSAP8 and HvSAP16, and Corresponding SNP Markers, Are Associated with Drought Tolerance in Barley Populations
- PMID: 34830037
- PMCID: PMC8617764
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms222212156
Expression of Specific Alleles of Zinc-Finger Transcription Factors, HvSAP8 and HvSAP16, and Corresponding SNP Markers, Are Associated with Drought Tolerance in Barley Populations
Abstract
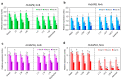
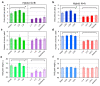
Two genes, HvSAP8 and HvSAP16, encoding Zinc-finger proteins, were identified earlier as active in barley plants. Based on bioinformatics and sequencing analysis, six SNPs were found in the promoter regions of HvSAP8 and one in HvSAP16, among parents of two barley segregating populations, Granal × Baisheshek and Natali × Auksiniai-2. ASQ and Amplifluor markers were developed for HvSAP8 and HvSAP16, one SNP in each gene, and in each of two populations, showing simple Mendelian segregation. Plants of F6 selected breeding lines and parents were evaluated in a soil-based drought screen, revealing differential expression of HvSAP8 and HvSAP16 corresponding with the stress. After almost doubling expression during the early stages of stress, HvSAP8 returned to pre-stress level or was strongly down-regulated in plants with Granal or Baisheshek genotypes, respectively. For HvSAP16 under drought conditions, a high expression level was followed by either a return to original levels or strong down-regulation in plants with Natali or Auksiniai-2 genotypes, respectively. Grain yield in the same breeding lines and parents grown under moderate drought was strongly associated with their HvSAP8 and HvSAP16 genotypes. Additionally, Granal and Natali genotypes with specific alleles at HvSAP8 and HvSAP16 were associated with improved performance under drought via higher 1000 grain weight and more shoots per plant, respectively.
Keywords: ASQ and Amplifluor markers; SNP plant genotyping; barley; drought; gene expression; grain yield and yield components; shoots number per plant; stress-associated genes; thousand grain weight; zinc-finger transcription factors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Dixit V.M., Green S., Sarma V., Holzman L.B., Wolf F.W., O’Rourke K., Ward P.A., Prochownik E.V., Marks R.M. Tumor necrosis factor-α induction of novel gene products in human endothelial cells including a macrophage-specific chemotaxin. J. Biol. Chem. 1990;265:2973–2978. doi: 10.1016/S0021-9258(19)39896-5. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Schuster A., Klein E., Neirinckx V., Knudsen A.M., Fabian C., Hau A.C., Dieterle M., Oudin A., Nazarov P.V., Golebiewska A., et al. AN1-type zinc finger protein 3 (ZFAND3) is a transcriptional regulator that drives Glioblastoma invasion. Nat. Commun. 2020;11:6366. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-20029-y. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

