Therapeutic Potential of Ursolic Acid in Cancer and Diabetic Neuropathy Diseases
- PMID: 34830043
- PMCID: PMC8621142
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms222212162
Therapeutic Potential of Ursolic Acid in Cancer and Diabetic Neuropathy Diseases
Abstract
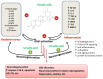
Ursolic acid (UA) is a pentacyclic triterpenoid frequently found in medicinal herbs and plants, having numerous pharmacological effects. UA and its analogs treat multiple diseases, including cancer, diabetic neuropathy, and inflammatory diseases. UA inhibits cancer proliferation, metastasis, angiogenesis, and induced cell death, scavenging free radicals and triggering numerous anti- and pro-apoptotic proteins. The biochemistry of UA has been examined broadly based on the literature, with alterations frequently having been prepared on positions C-3 (hydroxyl), C12-C13 (double bonds), and C-28 (carboxylic acid), leading to several UA derivatives with increased potency, bioavailability and water solubility. UA could be used as a protective agent to counter neural dysfunction via anti-oxidant and anti-inflammatory effects. It is a potential therapeutic drug implicated in the treatment of cancer and diabetic complications diseases provide novel machinery to the anti-inflammatory properties of UA. The pharmacological efficiency of UA is exhibited by the therapeutic theory of one-drug → several targets → one/multiple diseases. Hence, UA shows promising therapeutic potential for cancer and diabetic neuropathy diseases. This review aims to discuss mechanistic insights into promising beneficial effects of UA. We further explained the pharmacological aspects, clinical trials, and potential limitations of UA for the management of cancer and diabetic neuropathy diseases.
Keywords: clinical trials; diabetic neuropathy; inflammatory diseases; inhibitors; targeted therapy; ursolic acid.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Van Kiem P., Hang D.T., Nhiem N.X., Tai B.H., Anh H.L.T., Van Cuong P., Quang T.H., Van Minh C., Van Dau N., Kim Y.A., et al. Sesquiterpene derivatives from marine sponge Smenospongia cerebriformis and their anti-inflammatory activity. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2017;27:1525–1529. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2017.02.040. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

