Patient-Specific iPSC-Derived Neural Differentiated and Hepatocyte-like Cells, Carrying the Compound Heterozygous Mutation p.V1023Sfs*15/p.G992R, Present the "Variant" Biochemical Phenotype of Niemann-Pick Type C1 Disease
- PMID: 34830064
- PMCID: PMC8624182
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms222212184
Patient-Specific iPSC-Derived Neural Differentiated and Hepatocyte-like Cells, Carrying the Compound Heterozygous Mutation p.V1023Sfs*15/p.G992R, Present the "Variant" Biochemical Phenotype of Niemann-Pick Type C1 Disease
Abstract
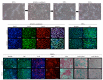
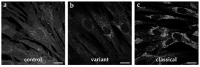
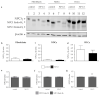
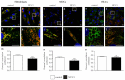
Niemann-Pick disease type C1 (NP-C1) is a rare lysosomal storage disorder caused by autosomal recessive mutations in the NPC1 gene. Patients display a wide spectrum on the clinical as well as on the molecular level, wherein a so-called "variant" biochemical phenotype can be observed. Here, we report an in vitro analysis of fibroblasts obtained from an NP-C1 patient carrying the undescribed compound heterozygous mutation p.V1023Sfs*15/p.G992R. Since NP-C1 is a neurovisceral disease and the patient suffers from severe neurological as well as hepatic symptoms, we extended our study to neural differentiated and hepatocyte-like cells derived from patient-specific induced pluripotent stem cells. We detected slightly increased intracellular cholesterol levels compared to the control cell line in fibroblasts, neural differentiated and hepatocyte-like cells, suggesting a "variant" biochemical phenotype. Furthermore, the total NPC1 protein, as well as post-ER glycoforms of the NPC1 protein, tended to be reduced. In addition, colocalization analysis revealed a mild reduction of the NPC1 protein in the lysosomes. The patient was diagnosed with NP-C1 at the age of 34 years, after an initial misdiagnosis of schizophrenia. After years of mild and unspecific symptoms, such as difficulties in coordination and concentration, symptoms progressed and the patient finally presented with ataxia, dysarthria, dysphagia, vertical supranuclear gaze palsy, and hepatosplenomegaly. Genetic testing finally pointed towards an NP-C1 diagnosis, revealing the so-far undescribed compound heterozygous mutation p.V1023Sfs*15/p.G992R in the NPC1 gene. In light of these findings, this case provides support for the p.G992R mutation being causative for a "variant" biochemical phenotype leading to an adult-onset type of NP-C1 disease.
Keywords: NP-C1; NPC1; cholesterol; filipin; iPSCs; induced pluripotent stem cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

