Protective Effects of Lactobacillus plantarum Lac16 on Clostridium perfringens Infection-Associated Injury in IPEC-J2 Cells
- PMID: 34830269
- PMCID: PMC8620398
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms222212388
Protective Effects of Lactobacillus plantarum Lac16 on Clostridium perfringens Infection-Associated Injury in IPEC-J2 Cells
Abstract
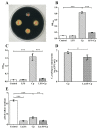
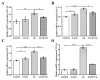
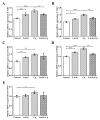
Clostridium perfringens (C. perfringens) causes intestinal injury through overgrowth and the secretion of multiple toxins, leading to diarrhea and necrotic enteritis in animals, including pigs, chickens, and sheep. This study aimed to investigate the protective effects of Lactobacillus plantarum (L. plantarum) Lac16 on C. perfringens infection-associated injury in intestinal porcine epithelial cell line (IPEC-J2). The results showed that L. plantarum Lac16 significantly inhibited the growth of C. perfringens, which was accompanied by a decrease in pH levels. In addition, L. plantarum Lac16 significantly elevated the mRNA expression levels of host defense peptides (HDPs) in IPEC-J2 cells, decreased the adhesion of C. perfringens to IPEC-J2 cells, and attenuated C. perfringens-induced cellular cytotoxicity and intestinal barrier damage. Furthermore, L. plantarum Lac16 significantly suppressed C. perfringens-induced gene expressions of proinflammatory cytokines and pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) in IPEC-J2 cells. Moreover, L. plantarum Lac16 preincubation effectively inhibited the phosphorylation of p65 caused by C. perfringens infection. Collectively, probiotic L. plantarum Lac16 exerts protective effects against C. perfringens infection-associated injury in IPEC-J2 cells.
Keywords: Clostridium perfringens; Lactobacillus plantarum; cellular injury; inflammation; intestinal barrier integrity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Protective effects of Lactobacillus plantarum on epithelial barrier disruption caused by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli in intestinal porcine epithelial cells.Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2016 Apr;172:55-63. doi: 10.1016/j.vetimm.2016.03.005. Epub 2016 Mar 5. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2016. PMID: 27032504
-
Protective Effects of Lactobacillus plantarum 16 and Paenibacillus polymyxa 10 Against Clostridium perfringens Infection in Broilers.Front Immunol. 2021 Feb 18;11:628374. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.628374. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33679724 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-21-5p targets PDCD4 to modulate apoptosis and inflammatory response to Clostridium perfringens beta2 toxin infection in IPEC-J2 cells.Dev Comp Immunol. 2021 Jan;114:103849. doi: 10.1016/j.dci.2020.103849. Epub 2020 Sep 1. Dev Comp Immunol. 2021. PMID: 32888967
-
Mechanisms of intestinal epithelial cell damage by Clostridiumperfringens.Anaerobe. 2024 Jun;87:102856. doi: 10.1016/j.anaerobe.2024.102856. Epub 2024 Apr 10. Anaerobe. 2024. PMID: 38609034 Review.
-
Clostridium perfringens type C necrotic enteritis in pigs: diagnosis, pathogenesis, and prevention.J Vet Diagn Invest. 2020 Mar;32(2):203-212. doi: 10.1177/1040638719900180. Epub 2020 Jan 20. J Vet Diagn Invest. 2020. PMID: 31955664 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Probiotic Bactolac alleviates depression-like behaviors by modulating BDNF, NLRP3 and MC4R levels, reducing neuroinflammation and promoting neural repair in rat model.Pflugers Arch. 2025 Jun;477(6):797-814. doi: 10.1007/s00424-025-03084-6. Epub 2025 Apr 26. Pflugers Arch. 2025. PMID: 40281288 Free PMC article.
-
Unraveling the pathogenic potential of the Pentatrichomonas hominis PHGD strain: impact on IPEC-J2 cell growth, adhesion, and gene expression.Parasite. 2024;31:18. doi: 10.1051/parasite/2024014. Epub 2024 Mar 26. Parasite. 2024. PMID: 38530211 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro evaluation of the immunomodulatory and wakame assimilation properties of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum strains from swine milk.Front Microbiol. 2024 Jan 26;15:1324999. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1324999. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38343714 Free PMC article.
-
Probiotic Characterization of Lactiplantibacillus paraplantarum SDN1.2 and Its Anti-Inflammatory Effect on Klebsiella pneumoniae-Infected Mammary Glands.Vet Sci. 2025 Apr 1;12(4):323. doi: 10.3390/vetsci12040323. Vet Sci. 2025. PMID: 40284825 Free PMC article.
-
Probiotic Bacillus subtilis LF11 Protects Intestinal Epithelium Against Salmonella Infection.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022 Feb 16;12:837886. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.837886. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35252040 Free PMC article.
References
-
- O’Brien D.K., Melville S.B. Effects of Clostridium perfringens Alpha-Toxin (PLC) and Perfringolysin O (PFO) on Cytotoxicity to Macrophages, on Escape from the Phagosomes of Macrophages, and on Persistence of C. perfringens in Host Tissues. Infect. Immun. 2004;72:5204–5215. doi: 10.1128/IAI.72.9.5204-5215.2004. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- No. LZ20C170002/Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang province, China
- No. 32072766/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- No. 31672460/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- No. 31472128/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- No. 2013AA102803D/National High-Tech R&D Program (863) of China
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

