Monoclonal Antibodies against Nucleocapsid Protein of SARS-CoV-2 Variants for Detection of COVID-19
- PMID: 34830291
- PMCID: PMC8623253
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms222212412
Monoclonal Antibodies against Nucleocapsid Protein of SARS-CoV-2 Variants for Detection of COVID-19
Abstract
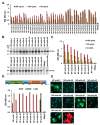
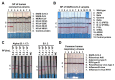
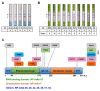
Mitigation strategies of the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic have been greatly hindered by the continuous emergence of SARS-CoV-2 variants. New sensitive, rapid diagnostic tests for the wide-spectrum detection of viral variants are needed. We generated a panel of 41 monoclonal antibodies against the SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein (NP) by using mice hybridoma techniques. Of these mAbs, nine exhibited high binding activities and were applied in latex-based lateral flow immunoassays (LFIAs). The LFIAs utilizing NP-mAb-7 and -40 had the best sensitivity and lowest limit of detection: 8 pg for purified NP and 625 TCID50/mL for the authentic virus (hCoV-19/Taiwan/4/2020). The specificity tests showed that the NP-mAb-40/7 LFIA strips did not cross-react with five human coronavirus strains or 20 other common respiratory pathogens. Importantly, we found that 10 NP mutants, including alpha (B.1.1.7), beta (B.1.351), gamma (P.1), and delta (B.1.617.2) variants, could be detected by NP-mAb-40/7 LFIA strips. A clinical study (n = 60) of the NP-mAb-40/7 LFIA strips demonstrated a specificity of 100% and sensitivity of 90% in infected individuals with cycle threshold (Ct) values < 29.5. These anti-NP mAbs have strong potential for use in the clinical detection of SARS-CoV-2 infection, whether the virus is wild-type or a variant of concern.
Keywords: COVID-19; LFIA; SARS-CoV-2; antibody; nucleocapsid protein; rapid test.
Conflict of interest statement
Related to the Acadecise antigen rapid test, Academia Sinica has received an EUA from the TFDA. Academia Sinica has material transfer agreements (MTAs) for anti-NP mAbs with Panion & BF Biotech Inc., and it has commissioned Panion & BF Biotech Inc. to develop and produce Acadecise antigen rapid test kits. The individual authors in this study declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Immunoassay Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Using Monoclonal Antibody Binding to Viral Nucleocapsid Protein.Microb Biotechnol. 2025 Feb;18(2):e70117. doi: 10.1111/1751-7915.70117. Microb Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 39989430 Free PMC article.
-
Highly specific monoclonal antibodies and epitope identification against SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein for antigen detection tests.Cell Rep Med. 2021 Jun 15;2(6):100311. doi: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2021.100311. Epub 2021 May 16. Cell Rep Med. 2021. PMID: 34027498 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid Biosensor of SARS-CoV-2 Using Specific Monoclonal Antibodies Recognizing Conserved Nucleocapsid Protein Epitopes.Viruses. 2022 Jan 27;14(2):255. doi: 10.3390/v14020255. Viruses. 2022. PMID: 35215848 Free PMC article.
-
Current status of the lateral flow immunoassay for the detection of SARS-CoV-2 in nasopharyngeal swabs.Biochem Med (Zagreb). 2021 Jun 15;31(2):020601. doi: 10.11613/BM.2021.020601. Biochem Med (Zagreb). 2021. PMID: 34140830 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SERS Based Lateral Flow Immunoassay for Point-of-Care Detection of SARS-CoV-2 in Clinical Samples.ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):2974-2995. doi: 10.1021/acsabm.1c00102. Epub 2021 Mar 17. ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2021. PMID: 35014387 Review.
Cited by
-
Transient Expression in HEK-293 Cells in Suspension Culture as a Rapid and Powerful Tool: SARS-CoV-2 N and Chimeric SARS-CoV-2N-CD154 Proteins as a Case Study.Biomedicines. 2023 Nov 14;11(11):3050. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11113050. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 38002050 Free PMC article.
-
Production of a Monoclonal Antibody to the Nucleocapsid Protein of SARS-CoV-2 and Its Application to ELISA-Based Detection Methods with Broad Specificity by Combined Use of Detector Antibodies.Viruses. 2022 Dec 21;15(1):28. doi: 10.3390/v15010028. Viruses. 2022. PMID: 36680068 Free PMC article.
-
Monoclonal antibodies against S2 subunit of spike protein exhibit broad reactivity toward SARS-CoV-2 variants.J Biomed Sci. 2022 Dec 22;29(1):108. doi: 10.1186/s12929-022-00891-2. J Biomed Sci. 2022. PMID: 36550570 Free PMC article.
-
Immunogenicity Evaluating of the Multivalent COVID-19 Inactivated Vaccine against the SARS-CoV-2 Variants.Vaccines (Basel). 2022 Jun 16;10(6):956. doi: 10.3390/vaccines10060956. Vaccines (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35746564 Free PMC article.
-
A highly sensitive nanobody-based immunoassay detecting SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein using all-recombinant reagents.Front Immunol. 2023 Jul 11;14:1220477. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1220477. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37497229 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Auwaerter P.M.D., Coronavirus COVID-19 (SARS-CoV-2) Johns Hopkins ABX Guide. The Johns Hopkins University. [(accessed on 11 November 2021)]. Available online: https://www.hopkinsguides.com/hopkins/view/Johns_Hopkins_ABX_Guide/54074....
-
- Andreadakis Z., Kumar A., Román R.G., Tollefsen S., Saville M., Mayhew S. The COVID-19 vaccine development landscape. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2020;19:305–306. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

