Diabetes and Colorectal Cancer Risk: A New Look at Molecular Mechanisms and Potential Role of Novel Antidiabetic Agents
- PMID: 34830295
- PMCID: PMC8622770
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms222212409
Diabetes and Colorectal Cancer Risk: A New Look at Molecular Mechanisms and Potential Role of Novel Antidiabetic Agents
Abstract
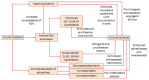
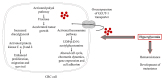
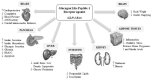
Epidemiological data have demonstrated a significant association between the presence of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) and the development of colorectal cancer (CRC). Chronic hyperglycemia, insulin resistance, oxidative stress, and inflammation, the processes inherent to T2DM, also play active roles in the onset and progression of CRC. Recently, small dense low-density lipoprotein (LDL) particles, a typical characteristic of diabetic dyslipidemia, emerged as another possible underlying link between T2DM and CRC. Growing evidence suggests that antidiabetic medications may have beneficial effects in CRC prevention. According to findings from a limited number of preclinical and clinical studies, glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1RAs) could be a promising strategy in reducing the incidence of CRC in patients with diabetes. However, available findings are inconclusive, and further studies are required. In this review, novel evidence on molecular mechanisms linking T2DM with CRC development, progression, and survival will be discussed. In addition, the potential role of GLP-1RAs therapies in CRC prevention will also be evaluated.
Keywords: glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists; hyperglycemia; inflammation; insulin resistance; oxidative stress; small dense LDL.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Treatment Strategy for Type 2 Diabetes with Obesity: Focus on Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists.Clin Ther. 2017 Jun;39(6):1244-1264. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2017.03.013. Epub 2017 May 16. Clin Ther. 2017. PMID: 28526416 Review.
-
Review of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus in patients with chronic kidney disease and their renal effects.J Diabetes. 2019 Dec;11(12):938-948. doi: 10.1111/1753-0407.12969. Epub 2019 Aug 14. J Diabetes. 2019. PMID: 31318152 Free PMC article. Review.
-
GLP-1RAs in type 2 diabetes: mechanisms that underlie cardiovascular effects and overview of cardiovascular outcome data.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2018 Dec 13;17(1):157. doi: 10.1186/s12933-018-0800-2. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2018. PMID: 30545359 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel skeletal effects of glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists.J Endocrinol. 2018 Jan;236(1):R29-R42. doi: 10.1530/JOE-17-0278. Epub 2017 Aug 30. J Endocrinol. 2018. PMID: 28855317 Review.
-
Role of GLP-1 Analogs in the Management of Diabetes and its Secondary Complication.Mini Rev Med Chem. 2021;21(20):3166-3182. doi: 10.2174/1389557521666210422114909. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 33888049 Review.
Cited by
-
Alteration of Metabolic Syndrome Is Associated with the Decreased Risk of Colorectal Cancer.J Clin Med. 2023 Jul 25;12(15):4889. doi: 10.3390/jcm12154889. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 37568291 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Advanced Glycation End Products on Dyslipidemia.Metabolites. 2023 Jan 3;13(1):77. doi: 10.3390/metabo13010077. Metabolites. 2023. PMID: 36677002 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metformin's role in lowering colorectal cancer risk among individuals with diabetes from the Southern Community Cohort Study.Cancer Epidemiol. 2024 Jun;90:102566. doi: 10.1016/j.canep.2024.102566. Epub 2024 Mar 21. Cancer Epidemiol. 2024. PMID: 38518387 Free PMC article.
-
High glucose inhibits autophagy and promotes the proliferation and metastasis of colorectal cancer through the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway.Cancer Med. 2024 Jun;13(11):e7382. doi: 10.1002/cam4.7382. Cancer Med. 2024. PMID: 38872380 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of hyperglycemia on the occurrence and prognosis of colorectal cancer.Am J Transl Res. 2024 May 15;16(5):2070-2081. doi: 10.62347/NYHH3132. eCollection 2024. Am J Transl Res. 2024. PMID: 38883369 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Saeedi P., Petersohn I., Salpea P., Malanda B., Karuranga S., Unwin N., Colagiuri S., Guariguata L., Motala A.A., Ogurtsova K., et al. Global and regional diabetes prevalence estimates for 2019 and projections for 2030 and 2045: Results from the International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas, 9th edition. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2019;157:107843. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2019.107843. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ling S., Brown K., Miksza J.K., Howells L., Morrison A., Issa E., Yates T., Khunti K., Davies M.J., Zaccardi F. Association of Type 2 Diabetes with Cancer: A Meta-analysis With Bias Analysis for Unmeasured Confounding in 151 Cohorts Comprising 32 Million People. Diabetes Care. 2020;43:2313–2322. doi: 10.2337/dc20-0204. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

