Diabetes and Colorectal Cancer Risk: A New Look at Molecular Mechanisms and Potential Role of Novel Antidiabetic Agents
- PMID: 34830295
- PMCID: PMC8622770
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms222212409
Diabetes and Colorectal Cancer Risk: A New Look at Molecular Mechanisms and Potential Role of Novel Antidiabetic Agents
Abstract
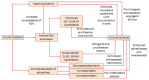
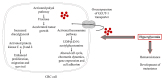
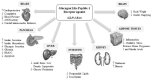
Epidemiological data have demonstrated a significant association between the presence of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) and the development of colorectal cancer (CRC). Chronic hyperglycemia, insulin resistance, oxidative stress, and inflammation, the processes inherent to T2DM, also play active roles in the onset and progression of CRC. Recently, small dense low-density lipoprotein (LDL) particles, a typical characteristic of diabetic dyslipidemia, emerged as another possible underlying link between T2DM and CRC. Growing evidence suggests that antidiabetic medications may have beneficial effects in CRC prevention. According to findings from a limited number of preclinical and clinical studies, glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1RAs) could be a promising strategy in reducing the incidence of CRC in patients with diabetes. However, available findings are inconclusive, and further studies are required. In this review, novel evidence on molecular mechanisms linking T2DM with CRC development, progression, and survival will be discussed. In addition, the potential role of GLP-1RAs therapies in CRC prevention will also be evaluated.
Keywords: glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists; hyperglycemia; inflammation; insulin resistance; oxidative stress; small dense LDL.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Saeedi P., Petersohn I., Salpea P., Malanda B., Karuranga S., Unwin N., Colagiuri S., Guariguata L., Motala A.A., Ogurtsova K., et al. Global and regional diabetes prevalence estimates for 2019 and projections for 2030 and 2045: Results from the International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas, 9th edition. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2019;157:107843. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2019.107843. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ling S., Brown K., Miksza J.K., Howells L., Morrison A., Issa E., Yates T., Khunti K., Davies M.J., Zaccardi F. Association of Type 2 Diabetes with Cancer: A Meta-analysis With Bias Analysis for Unmeasured Confounding in 151 Cohorts Comprising 32 Million People. Diabetes Care. 2020;43:2313–2322. doi: 10.2337/dc20-0204. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

