Immunomodulation and Reduction of Thromboembolic Risk in Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Trials
- PMID: 34830648
- PMCID: PMC8617689
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm10225366
Immunomodulation and Reduction of Thromboembolic Risk in Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Trials
Abstract
Background: We aimed to investigate the potential beneficial effect of immunomodulation therapy on the thromboembolic risk in hospitalized COVID-19 patients.
Methods: We searched PubMed and Scopus for randomized trials reporting the outcomes of venous thromboembolism (VTE), ischemic stroke or systemic embolism, myocardial infarction, any thromboembolic event, and all-cause mortality in COVID-19 patients treated with immunomodulatory agents. Odds ratios (OR) and 95% confidence intervals (CI) were calculated using the Mantel-Haenszel random effects method.
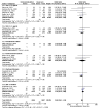
Results: Among 8499 patients hospitalized with COVID-19, 4638 were treated with an immunomodulatory agent, 3861-with usual care only. Among the patients prescribed immunomodulatory agents, there were 1.77 VTEs per 100 patient-months compared to 2.30 among those treated with usual care (OR: 0.84, 95% CI: 0.61-1.16; I2: 0%). Among the patients who received an interleukin 6 (IL-6) antagonist, VTEs were reported in 12 among the 1075 patients compared to 20 among the 848 receiving the usual care (OR: 0.52, 95% CI: 0.22-1.20; I2: 6%). Immunomodulators as an add-on to usual care did not reduce the risk of stroke or systemic embolism (OR: 1.10, 95% CI: 0.50-2.40; I2: 0%) or of myocardial infarction (OR: 1.06, 95% CI: 0.47-2.39; I2: 0%) and there was a nonsignificant reduction in any thromboembolic event (OR: 0.86, 95% CI: 0.65-1.14; I2: 0%).
Conclusions: We did not identify a statistically significant effect of immunomodulation on prevention of thromboembolic events in COVID-19. However, given the large effect estimate for VTE prevention, especially in the patients treated with IL-6 antagonists, we cannot exclude a potential effect of immunomodulation.
Keywords: COVID-19; anakinra; hydroxycholoroquine; immunomodulation; thromboembolism; tocilizumab.
Conflict of interest statement
Dimitrios Sagris: nothing to disclose. Matilda Florentin: nothing to disclose. Panagiotis Tasoudis: nothing to disclose. Eleni Korompoki has received speaker’s honoraria from Amgen and BMS/Pfizer, travel grants from Bayer, contributed to the advisory board of BMS/Pfizer. Nikolaos Gatselis: nothing to disclose. Evangelos J. Giamarellos-Bourboulis has received honoraria from Abbott CH, bioMérieux, Brahms GmbH, GSK, InflaRx GmbH, and XBiotech Inc; independent educational grants from Abbott CH, AxisShield, bioMérieux Inc, InflaRx GmbH, Johnson & Johnson, and XBiotech Inc.; and funding from the Horizon2020 Marie-Curie Project European Sepsis Academy (granted to the National and Kapodistrian University of Athens), and the Horizon 2020 European Grants ImmunoSep and RISKinCOVID (granted to the Hellenic Institute for the Study of Sepsis). Haralampos Milionis declares receiving honoraria, consulting fees, and nonfinancial support from healthcare companies including Amgen, Bayer, Mylan, MSD, Pfizer, Sanofi, and Servier. James Douketis discloses consulting fees from Janssen, BMS, and Servier and speaking fees from Bayer, BMS, Pfizer, Sanofi, Leo Pharma. Monies from these sources are deposited into university- or hospital foundation-based research accounts. Alex C Spyropoulos discloses consulting fees and research support from Janssen and Boehringer Ingelheim and consulting fees from Bayer, BMS, Portola, Sanofi, the ATLAS Group. George N Dalekos is an advisor or lecturer for Ipsen, Pfizer, Genkyotex, Novartis, Sobi, received research grants from Abbvie, Gilead and has served as PI in studies for Abbvie, Novartis, Gilead, Novo Nordisk, Genkyotex, Regulus Therapeutics Inc, Tiziana Life Sciences, Bayer, Astellas, Pfizer, Amyndas Pharmaceuticals, CymaBay Therapeutics Inc., Sobi, and Intercept Pharmaceuticals. George Ntaios discloses speaker fees/participation in the advisory board/research support from Abbott, Amgen, Bayer, BMS, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Pfizer, Sanofi. All fees are paid to his institution (University of Thessaly).
Figures



References
-
- Chi G., Lee J.J., Jamil A., Gunnam V., Najafi H., Memar Montazerin S., Shojaei F., Marszalek J. Venous Thromboembolism among Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19 Undergoing Thromboprophylaxis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2020;9:2489. doi: 10.3390/jcm9082489. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Klok F.A., Kruip M., van der Meer N.J.M., Arbous M.S., Gommers D., Kant K.M., Kaptein F.H.J., van Paassen J., Stals M.A.M., Huisman M.V., et al. Incidence of thrombotic complications in critically ill ICU patients with COVID-19. Thromb. Res. 2020;191:145–147. doi: 10.1016/j.thromres.2020.04.013. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Berger J.S., Kunichoff D., Adhikari S., Ahuja T., Amoroso N., Aphinyanaphongs Y., Cao M., Goldenberg R., Hindenburg A., Horowitz J., et al. Prevalence and Outcomes of D-Dimer Elevation in Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2020;40:2539–2547. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.120.314872. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

