Dysregulation of Translation Factors EIF2S1, EIF5A and EIF6 in Intestinal-Type Adenocarcinoma (ITAC)
- PMID: 34830804
- PMCID: PMC8616251
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers13225649
Dysregulation of Translation Factors EIF2S1, EIF5A and EIF6 in Intestinal-Type Adenocarcinoma (ITAC)
Abstract
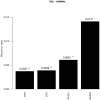
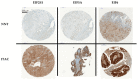
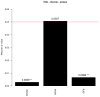
Intestinal-type adenocarcinoma (ITAC) is a rare cancer of the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses that occurs sporadically or secondary to exposure to occupational hazards, such as wood dust and leather. Eukaryotic translation initiation factors have been described as promising targets for novel cancer treatments in many cancers, but hardly anything is known about these factors in ITAC. Here we performed in silico analyses, evaluated the protein levels of EIF2S1, EIF5A and EIF6 in tumour samples and non-neoplastic tissue controls obtained from 145 patients, and correlated these results with clinical outcome data, including tumour site, stage, adjuvant radiotherapy and survival. In silico analyses revealed significant upregulation of the translation factors EIF6 (ITGB4BP), EIF5, EIF2S1 and EIF2S2 (p < 0.05) with a higher arithmetic mean expression in ITAC compared to non-neoplastic tissue (NNT). Immunohistochemical analyses using antibodies against EIF2S1 and EIF6 confirmed a significantly different expression at the protein level (p < 0.05). In conclusion, this work identifies the eukaryotic translation initiation factors EIF2S1 and EIF6 to be significantly upregulated in ITAC. As these factors have been described as promising therapeutic targets in other cancers, this work identifies candidate therapeutic targets in this rare but often deadly cancer.
Keywords: biomarkers; sinonasal adenocarcinoma of the intestinal type (ITAC); translation factors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The Role of SATB2 as a Diagnostic Marker of Sinonasal Intestinal-type Adenocarcinoma.Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol. 2018 Feb;26(2):140-146. doi: 10.1097/PAI.0000000000000388. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol. 2018. PMID: 27258560
-
Intestinal and non-intestinal nasal cavity adenocarcinoma: Impact of wood dust exposure.Eur Ann Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Dis. 2018 Dec;135(6):383-387. doi: 10.1016/j.anorl.2018.08.012. Epub 2018 Sep 7. Eur Ann Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Dis. 2018. PMID: 30201443
-
Genome-wide somatic mutation analysis of sinonasal adenocarcinoma with and without wood dust exposure.Genes Environ. 2024 May 6;46(1):12. doi: 10.1186/s41021-024-00306-8. Genes Environ. 2024. PMID: 38711096 Free PMC article.
-
Intestinal-type sinonasal adenocarcinomas: The road to molecular diagnosis and personalized treatment.Head Neck. 2016 Oct;38(10):1564-70. doi: 10.1002/hed.24416. Epub 2016 May 25. Head Neck. 2016. PMID: 27224655 Review.
-
Tumor Markers and Their Prognostic Value in Sinonasal ITAC/Non-ITAC.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Jun 15;15(12):3201. doi: 10.3390/cancers15123201. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37370810 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Tumors of the Nose and Paranasal Sinuses: Promoting Factors and Molecular Mechanisms-A Systematic Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 31;24(3):2670. doi: 10.3390/ijms24032670. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36768990 Free PMC article.
-
EIF2S1 Silencing Impedes Neuroblastoma Development Through GPX4 Inactivation and Ferroptosis Induction.Int J Genomics. 2024 Oct 19;2024:6594426. doi: 10.1155/2024/6594426. eCollection 2024. Int J Genomics. 2024. PMID: 39465005 Free PMC article.
-
EIF2S2 as a prognostic marker and therapeutic target in glioblastoma: insights into its role and downstream mechanisms.Cancer Cell Int. 2025 Apr 2;25(1):126. doi: 10.1186/s12935-025-03762-6. Cancer Cell Int. 2025. PMID: 40176031 Free PMC article.
-
Signaling Pathways mTOR and ERK as Therapeutic Targets in Sinonasal Intestinal-Type Adenocarcinoma.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Oct 12;24(20):15110. doi: 10.3390/ijms242015110. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37894790 Free PMC article.
-
A multiscale functional map of somatic mutations in cancer integrating protein structure and network topology.Nat Commun. 2025 Jan 24;16(1):975. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-54176-3. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 39856048 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nicolai P., Schreiber A., Villaret A.B., Lombardi D., Morassi L., Raffetti E., Donato F., Battaglia P., Turri–Zanoni M., Bignami M., et al. Intestinal Type Adenocarcinoma of the Ethmoid: Outcomes of a Treatment Regimen Based on Endoscopic Surgery with or without Radiotherapy. Head Neck. 2016;38:E996–E1003. doi: 10.1002/hed.24144. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

