Oral Contraceptive Use and Breast Cancer Risk Assessment: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Case-Control Studies, 2009-2020
- PMID: 34830807
- PMCID: PMC8616467
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers13225654
Oral Contraceptive Use and Breast Cancer Risk Assessment: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Case-Control Studies, 2009-2020
Abstract
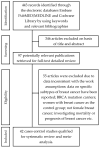
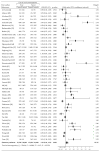
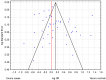
To perform a meta-analysis of case-control studies that addressed the association between oral contraceptive pills (OC) use and breast cancer (BrCa), PubMED (MEDLINE), Embase, and the Cochrane Library were searched to identify case-control studies of OC and BrCa published between 2009 and 2020. We used the DerSimonian-Laird method to compute pooled odds ratios (ORs) and confidence intervals (CIs), and the Mantel-Haenszel test to assess the association between OC use and cancer. Forty-two studies were identified that met the inclusion criteria and we included a total of 110,580 women (30,778 into the BrCa group and 79,802 into the control group, of which 15,722 and 38,334 were using OC, respectively). The conducted meta-analysis showed that the use of OC was associated with a significantly increased risk of BrCa in general, OR = 1.15, 95% CI: 1.01 to 1.31, p = 0.0358. Regarding other risk factors for BrCa, we found that increased risk was associated significantly with early menarche, nulliparous, non-breastfeeding, older age at first parity, postmenopause, obesity, smoking, and family history of BrCa. Despite our conclusion that birth control pills increase the cancer risk being supported by extensive previous studies and meta-analyzes, further confirmation is required.
Keywords: breast cancer; breast malignancies; oral contraceptives; risk; risk factors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Oral Contraceptive Use and Breast Cancer Risk According to Molecular Subtypes Status: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Case-Control Studies.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Jan 23;14(3):574. doi: 10.3390/cancers14030574. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35158842 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oral Contraceptive Use and Breast Cancer Risk for BRCA1 and BRCA2 Mutation Carriers: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Case-Control Studies.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Sep 29;14(19):4774. doi: 10.3390/cancers14194774. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36230696 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oral contraceptive use as a risk factor for premenopausal breast cancer: a meta-analysis.Mayo Clin Proc. 2006 Oct;81(10):1290-302. doi: 10.4065/81.10.1290. Mayo Clin Proc. 2006. PMID: 17036554
-
Breast cancer among young U.S. women in relation to oral contraceptive use.J Natl Cancer Inst. 1994 Apr 6;86(7):505-14. doi: 10.1093/jnci/86.7.505. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1994. PMID: 8133534
-
Use of oral contraceptives and risk of breast cancer in young women.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 1998 Jul;50(2):175-84. doi: 10.1023/a:1006037823178. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 1998. PMID: 9822222
Cited by
-
Oral Contraceptive Use and Breast Cancer Risk According to Molecular Subtypes Status: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Case-Control Studies.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Jan 23;14(3):574. doi: 10.3390/cancers14030574. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35158842 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epidemiological breast cancer prediction by country: A novel machine learning approach.PLoS One. 2024 Aug 14;19(8):e0308905. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0308905. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39141659 Free PMC article.
-
Risk of Gynecological Cancers in Women With Polycystic Ovary Syndrome and the Pathophysiology of Association.Cureus. 2023 Apr 7;15(4):e37266. doi: 10.7759/cureus.37266. eCollection 2023 Apr. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37162768 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oral Contraceptive Use and Breast Cancer Risk for BRCA1 and BRCA2 Mutation Carriers: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Case-Control Studies.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Sep 29;14(19):4774. doi: 10.3390/cancers14194774. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36230696 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Estrogens and the risk of breast cancer: A narrative review of literature.Heliyon. 2023 Sep 17;9(9):e20224. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e20224. eCollection 2023 Sep. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37809638 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- The Cancer Atlas: Breast Cancer Accounts for Almost a Quarter of New Cancer Cases among Women. [(accessed on 12 March 2021)]. Available online: https://canceratlas.cancer.org/wp-content/uploads/2019/09/CA3_BreastCanc....
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

