Correlation of Soluble CD44 Expression in Saliva and CD44 Protein in Oral Leukoplakia Tissues
- PMID: 34830890
- PMCID: PMC8616328
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers13225739
Correlation of Soluble CD44 Expression in Saliva and CD44 Protein in Oral Leukoplakia Tissues
Abstract
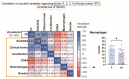
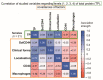
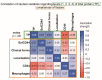
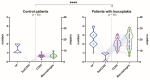
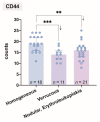
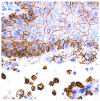
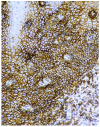
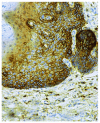
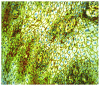
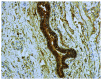
The aim of this study was to determine whether and how pan-CD44 protein expression in leukoplakia tissues correlates with positive SolCD44 test presence and their role in oral leukoplakia. SolCD44 and total protein expression in saliva were determined using an OncAlert® Oral Cancer Rapid test. Comparison of paired associations of total protein, SolCD44, mean number of CD44 expressed epithelial layers in leukoplakia tissue, and macrophages below the basement membrane between control group and patients with leukoplakia showed statistically significant results (p < 0.0001). It is shown that the total protein indicates low or elevated risk of possible malignant transformation processes in leukoplakia. Statistically significant differences between higher total protein level and clinical forms of oral leukoplakia (p < 0.0001), as well as CD44-labeled epithelial cell layer decrease (p < 0.0001), were found. This possibly points to the onset of the stemness loss in leukoplakia tissue. CD9 antigen expression in the exosomes of the oral epithelium explained the intercellular flow of SolCD44 and other fluids in the leukoplakia area. We conclude that the OncAlert® Oral Cancer Rapid test is a valuable screening method in daily clinical practice, in terms of complementing clinical diagnostics methods and to assess the potential for early malignancy.
Keywords: CD44 antigen; exosomes; oral leukoplakia; soluble CD44; total protein.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Diz P., Meleti M., Diniz-Freitas M., Vescovi P., Warnakulasuriya S., Johnson N.W., Kerr A.R. Oral and pharyngeal cancer in Europe: Incidence, mortality and trends as presented to the Global Oral Cancer Forum. Transl. Res. Oral Oncol. 2017;2:2057178X17701517. doi: 10.1177/2057178X17701517. - DOI
-
- Roza A.L.O.C., Kowalski L.P., William W.N., de Castro G., Chaves A.L.F., Araújo A.L.D., Ribeiro A.C.P., Brandão T.B., Lopes M.A., Vargas P.A., et al. Oral leukoplakia and erythroplakia in young patients: A systematic review. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. 2021;131:73–84. doi: 10.1016/j.oooo.2020.09.002. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

